Amyloidosis Definition
Amyloidosis is a condition where a group of abnormal protein deposits in tissues organ thus affecting their shape and their function.
What is Amyloidosis?
The Amyloidosis is a life threatening condition where some abnormal protein called amyloids builds up in tissues and organs all throughout the body. These amyloids which have been folded abnormally do not break down as easily as normal proteins thus a collected amyloids can cause tissue organs to stop functioning properly resulting to the condition known as amyloidosis.
Furthermore, there are approximately 30 different types of proteins that can peculiarly fold and form amyloid therefore causing to give rise to different types of amyloidosis.
Types
Localized Amyloidosis
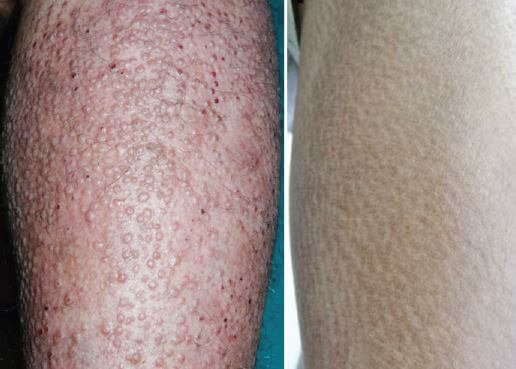
Abnormal protein or amyloids that deposited occasionally that only affects one part of the body. This is known also as Organ-Specific Amyloidosis. (Example; Cutaneous Amyloidosis- which affects the skin)
(Primary) Systemic “AL” Amyloidosis
amyloids are being deposited and distributed into different body organ such as kidney, heart, liver and nerves. The primary Amyloidosis occurs without a known cause but it is usually experienced by people with multiple myeloma (blood cancer). Since the Amyloidosis is systemic it means it affects the entire body. Furthermore, the primary protein that responsible for systemic amyloidosis is the AL stands for “amyloid light chains.”
(Secondary) Systemic “AA” Amyloidosis
The “AA” stands for an amyloid type A protein that causes the secondary systemic amyloidosis. This condition is the result of the chronic inflammatory diseases such as arthritis, Lupus, tuberculosis, rheumatoid, Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis (Inflamatory Bowel diseases) and other types of cancer. In many cases, the primary organs that invade by this Secondary AA Amyloidosis are the kidneys, spleen, liver, adrenal gland and lymph nodes.
Dialysis Related Amyloidosis
This other type of amyloidosis affects mostly older people who undergo dialysis treatment for more than five years. This DRA or Dialysis Related Amyloidosis is caused by deposits of beta-microglobulin that form in the blood. Therefore, it affects mostly the bones, joints and tendons.
Hereditary or Familial Amyloidosis
This condition is rare but can develop by passing the conditions through gene inheritance. This is because of the abnormal amyloid transthyretin (TTR) protein which is form in the liver, specific protein that most common form of hereditary amyloidosis.
Senile Systemic Amyloidosis (SSA)
This ailment is caused by deposited TTR, the heart and other related tissues. Statistically, there are 600 new cases of amyloidosis have been diagnoses in the United Kingdom alone every year. Surprisingly, the amyloidosis condition mostly suffered in older people.
Causes
The cause of Amyloidosis is not generally understood but Genes may play as culprit to cause abnormal folds of proteins.
Generally, the amyloidosis is caused by protein capability to become soluble. The proteins are become insoluble thus leading to become stored in organs and tissues. Once the accumulated amyloids deposited in the tissue they stuck in spaces between cells. Therefore, it causes some medical complications and worst lead to a life threating condition.
Risk Factors
Since Amyloidosis is linked with gene mutation, the high risk factor are also relates to genetic inheritance with their ancestors. Other factors include
- Age – people who are over 60 years old are most prone to develop Amyloidosis
- Gender – Interestingly, male orientation is a risk factor for Amyloidosis. According to MedecineNet, about 70% people with Primary Systemic AL Amyloidosis are often affected the males than Females.
Medical Conditions
Kidney Failure
Kidney is primarily responsible for filtering waste and toxins from the blood and releases it in a form of urine. Once an amyloid protein deposited in the kidney organ it makes them to perform its filtering mechanism. Therefore, malfunction of the kidney can make the body susceptible for toxicities and dangerous substances brought by blood that can easily build up in the body.
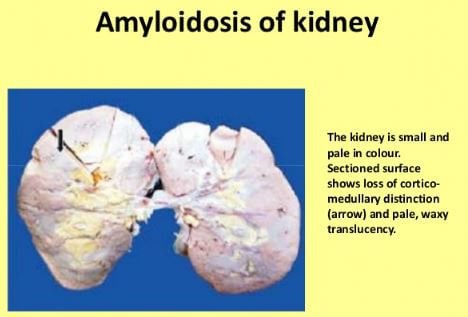
Some clinical manifestations can be seen as a sign of Kidney failure is the swelling of the feet and ankles, puffiness around the eyes, and presence of high protein presence in the urine sample.
Cardiac Ailment
Once the heart deposited by amyloid proteins it can make the heart muscle become firm, weak and affect the electrical cardiac rhythm. As a result of insufficient flow of blood going to the heart system. When that happens, the heart will stop its pumping mechanism and worst lead to death. Some cardiac experts rule out the amyloidosis with the shortness of breath during some light physical activities, irregular heartbeat, some signs of heart problem.
Nervous System
Common neurological complications of amyloidosis is the abnormality of “peripheral nerves.” The condition happens when amyloid protein deposits in the nervous system causing a wreckage of nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. Importantly, these peripheral nerves are primary responsible for carrying the information between the brain and central nervous system going to the rest of the body.
For instance, tasting a spicy food perceive by your brain to have hot sensation on your taste buds. If Amyloidosis affects the nerves, you will probably experience some difficulties such as, controlling bowel movement, balancing difficulty, excessive sweating, paresthesias (unusual sensations), vomiting, constipation, sexual problem, numbness, tingling, weakness of arms and legs.
Gastrointestinal (GI) Problem
Amyloid protein that form along the gastrointestinal tract can cause digestion and absorption problem of food nutrients, causing for having diarrhea, constipation, bleeding along the GI tract, stomach pain, rapid weight loss, nausea and decreased in appetite.
Signs and Symptoms
The symptoms of Amyloidosis may vary depending on the specific organs that are affected by amyloid protein. A particular individual may experience some of the general symptoms below;
- Abnormal cardiac heartbeat
- Swollen tongue known as Macroglossia
- Over fatigue
- Numbness of the hands or feet
- Shortness of breath
- Skin changes
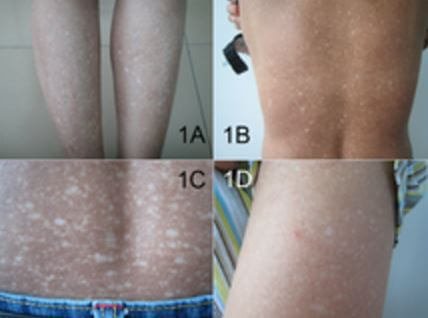
- Weakness of hand gripping
- Frequent diarrhea
- Rapid weight loss
- Swallowing difficulties
- Joint Pain
- Hoarseness of voice
- Lessen urine output
Diagnosis
In order to accurately rule out the possibility of Amyloidosis health experts perform diagnostic testing such as;
Biopsy
A tissue will be extracted from a specific organ such as abdominal fat, bone marrow, liver, spleen or kidney. Tissue analysis helps to rule out and exactly determine the type of amyloid deposit.
Laboratory Tests
Fluids are the primary test subjects such as the blood and urine to check if there is abnormal protein develops in the organ.
Imaging Tests
Images of the specific body organ that is affected by amyloidosis can help to evaluate the severity of diseases. For instance, ECG or echocardiogram to assess the size and operational status of the heart. Imaging test can also go further to examine liver or spleen to rule out the possibility of amyloidosis.
Medical History Background
Doctor will undergo first prior to some diagnostic test such as by asking your family history if there are some cases of amyloidosis or other types of common diseases like hypertension, kidney problem, Heart ailment etc.
Others
- Abdominal Fat pad aspiration
- Abdominal Ultrasound
- Kidney Function Test
- Rectal Mucosa biopsy
Treatment
Treating for Amyloidosis is still neither no cure nor clinical trials been going. However, treating the secondary forms of Amyloidosis can be avoided by remediating the underlying diseases associated with inflammation.
- Chemotherapy- helps to remove the substances that causes to amyloid formation.
- Stem Cell Transplant
- Pain Medication- intake of anti-inflammatory drugs to treat rheumatoid arthritis.
- Fluid retention Medication (diuretic drugs)- removing the excess water from the body
- Low salt intake- diet modification and abstaining for salt especially for those who have Gastrointestinal Tract problem
- Blood-thinning
- Transplant- such as liver transplantation may be the best option due to the protein that causes the hereditary amyloidosis.
SOURCES:
- http://www.cancer.net/cancer-types/amyloidosis/symptoms-and-signs
- http://www.medicinenet.com/amyloidosis/page4.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000533.htm
- http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/amyloidosis/basics/definition/con-20024354
- http://www.webmd.com/cancer/lymphoma/amyloidosis-symptoms-causes-treatments#4
- http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/amyloidosis/Pages/Introduction.aspx
