Cardiac Tamponade Definition
Cardiac tamponade is a condition where fluids and blood accumulates in the pericardium, which is a thin double sac that surrounds your heart. This exerts a lot of pressure on your heart. The pressure makes it harder for your heart to function properly as well as it restricts the heart ventricles from expanding fully. When this occurs, your heart can’t pump adequate blood around your body which can lead to failure of organs, shock and even death1, 3.
Cardiac tamponade is a life-threatening condition and can cause death if left untreated. If you suspect to have this condition, seek urgent medical attention.
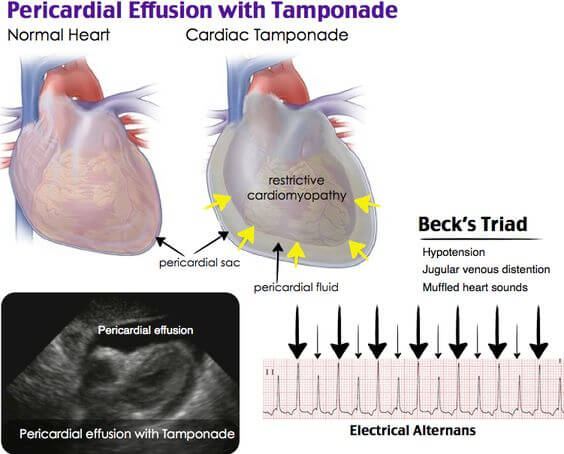
Fluid Within Pericardium. Change in ECG Pattern
Causes
Cardiac tamponade can occur as a result of many causes such as1, 4, 5
Infections
Infections that occur in your body can spread and reach your heart. This can cause blood and fluids to accumulate in the pericardium sac.
Tumors
Cancer that develops in any part of your body such as breast cancer can spread and affect the pericardium sac.
Autoimmune diseases
Autoimmune disorders occur when your immune system wrongly attacks organs and tissues in your body such as pericardium sac. The damaged pericardium sac may trap blood and fluids which leads to cardiac tamponade. An example of autoimmune disease is lupus.
Trauma
Trauma or any form of injury to your chest can cause blood and fluids to buildup in pericardium sac. Examples of traumas include being involved in a vehicle accident that affects your chest. Being stabbed or shot in your chest can also cause fluid and blood to accumulate in the pericardium sac. Another trauma to your chest occurs during insertion of catheter in your chest.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is used to eliminate cancerous cells. This method uses radiation which can destroy pericardium sac if cancer exists in your chest.
Hypothyroidism
This is a condition where thyroid gland produces inadequate thyroid hormones. Insufficient amount of thyroid hormones affects many of your body function such as metabolism.
Kidney failure
Kidney is responsible for filtering blood. Sometimes toxic materials may overwhelm it and impair its function. Kidney failure can also occur as a result of kidney stones or kidney infection. Kidney failure causes fluid and blood to accumulate in the pericardial sac leading to cardiac tamponade.
Surgery
Surgery done on your heart can damage blood vessels which bleed causing blood to accumulate in the pericardium sac. In some cases, during surgery, the heart of the patient is manipulated which might cause bleeding that exerts pressure on the heart.
Other causes of cardiac tamponade are
- Heart attack
- Pericarditis, a condition that causes pericardium to become inflamed.
Symptoms
Patients suffering from Cardiac tamponade exhibit the following symptoms6:
- Patients feel pain in their neck which can spread to other areas of the body such as shoulders, back or neck. They feel general body weaknesses and their blood pressure is usually low. Patients appear restless and anxious. In some cases, a patient might faint or feel dizzy
- Patients may find it difficult to breathe or taking deep breaths or breathe very fast. They feel uncomfortable but this is relieved when the patient sits down or leans forward.
Diagnosis
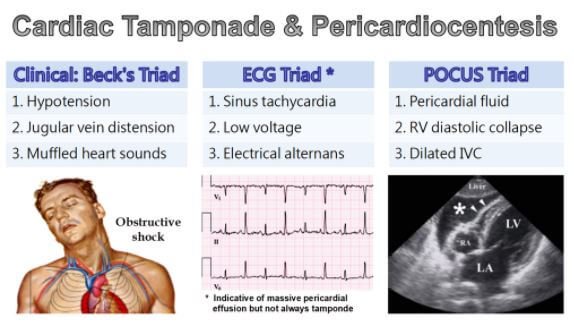
Cardiac tamponade is diagnosed through a physical exam and other clinical tests. In physical exam, your doctor looks for three signs that show you have cardiac tamponade. These signs are: weak pulse and low blood pressure which occurs when blood pumped from the heart is inadequate, a faster heartbeat which is combined with abnormal heart sounds, and enlarged veins in your neck which develop as a result of difficult of returning blood to your heart.
Your doctor can order the following tests to confirm diagnosis of cardiac tamponade:
Echocardiogram
This is a test done to take ultrasound of your heart. This test is used by your doctor to detect if your pericardium is enlarged or ventricles have collapsed due to insufficient blood.
Chest X-rays
X-rays done on the chest are important because they may show if the heart is enlarged.
Computed tomography scan
CT scans of your thoracic can help your doctor identify changes in your heart or buildup of fluids in the chest.
Magnetic resonance Imaging
MRI scan of your heart can assist your doctor understand flow of blood. The scan can also reveal if your heart and surrounding areas have problems.
Treatment
Treatment for cardiac tamponade aims at easing pressure on the patients’ heart and treating the cause properly. The first treatment ensures that the patient is stabilized.
Cardiac tamponade is a condition that needs urgent medical attention to drain out fluids from the pericardial sac. All patients with this condition receive the following treatment options:
- Oxygen: Patients are given oxygen to ensure they have sufficient amounts of oxygen in their body.
- They are also given either isotonic chloride solution or dextran to maintain adequate intravascular volume.
- Rest: The patient is offered enough bed rest with his/her leg raised to facilitate blood flow to the heart.
Once a patient has received the above treatment, your doctor can order any of the following medical procedures to drain out fluids from the pericardial sac:
- Subxiphoid percutaneous drainage: In this procedure, your doctor inserts a needle which points towards your left shoulder to remove fluids in the pericardial sac.
- Pericardiocentesis: This procedure is performed in the medical laboratory. Your doctor uses echocardiogram to perform the procedure to drain out the fluid from the pericardial sac.
- Percutaneous balloon pericardiotomy: In this procedure, your doctor uses a balloon to create a pericardial window to remove the fluid.
- Surgery: In severe cases, your doctor can order surgery to remove part of the pericardium sac that is damaged.
Patients with recurrent cardiac tamponade or those who are unstable are treated with the following medical procedure:
- Your doctor can perform surgery between intrapleural space and pericardial cavity to improve communication. Pericardiotomy or open thoracotomy may also be used to drain fluid out of the pericardial space.
Reference List
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/152083-treatment#d11
- https://www.healthline.com/health/cardiac-tamponade#treatment5
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000194.htm
- https://acls.com/free-resources/knowledge-base/pea-asystole/what-is-cardiac-tamponade
- https://patient.info/doctor/cardiac-tamponade
- Cardiac tamponade. Available at http://www.msdmanuals.com/professional/injuries-poisoning/thoracic-trauma/cardiac-tamponade
