What is Bibasilar Atelectasis?
Atelectasis is defined as the collapse of the lungs either partially or in entirety. The condition develops after the tiny air sacs known as alveoli found in the lungs deflate. It is a complication that can occur after having surgery, but is could also occur due to other respiratory complications for example, inhaling of foreign objects, presence of lung tumors, development of cystic fibrosis, build up of fluid within the lung, chest injuries, and respiratory weakness. Depending on the cause, the amount of tissue involved may vary. When you have atelectasis, it can make breathing to be difficulty, and the individual may have lower levels of oxygen, especially if there is presence of lung disease. Also treatment will depend on the cause of the condition and its severity.1,2,3,4
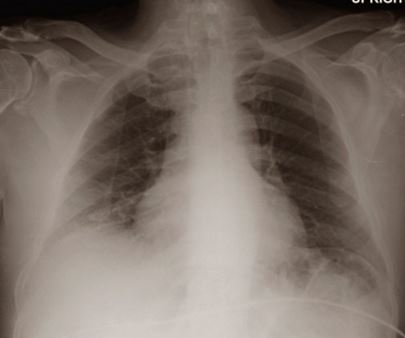
Bibasilar atelectasis is when the collapse involves the lower parts of the lungs. Bibasilar atelectasis may be similar to pneumothorax, however, the two conditions are different and arise in different situations. That being said, it is important to know that pneumothorax may contribute to bibasilar atelectasis.1,2,3,4
Lung Lobes and Alveoli
In humans, the lungs have smaller sections divided by fissures and these are referred to as the lung lobes. There are three lobes within the right lung while the left lung has two lobes. The reason there are three lobes within the right lung and only two in the left lung is because the latter is a little smaller compared to the former. The left lung has to make some room for the heart or the cardiac notch within the left part of the thoracic cavity. That’s why it is smaller in size and has only two lobes.10
The function of the lung lobes is to receive oxygen-rich air when it moves down the airways, they also house or host the oxygen-carbon dioxide exchange within the alveoli. In life-threatening situations, it is possible for surgeons to remove a lobe through lobectomy, especially if an individual has a serious health condition like lung cancer or tuberculosis. The removal of the lobe may affect the capacity of the lung, but a person can still lead a normal life. 10
In the lungs, there are tiny air sacs known as alveoli that are shaped like balloons and they contain blood vessels that are arranged in clusters. When there is obstruction that affects the airflow as happens with bibasilar atelectasis, it causes the alveoli to abnormally deflate. Mostly, bibasilar atelectasis affects the bottom parts of the lungs or the lower lobes. A person with bibasilar atelectasis may have a life-threatening situation because there is lack of oxygen travelling to vital body organs.2
Types of Bibasilar Atelectasis
There are different types of atelectasis and they are named according to the biological mechanisms that contribute to the collapse of the lungs.2
Resorptive atelectasis
This may also be referred to as obstructive atelectasis, and it is caused by obstruction of the airways. In this situation, there is blood flow, however, atelectasis will result because there is absorption of nitrogen and oxygen.
Relaxation atelectasis
With this type of atelectasis, it occurs where there is loss of negative pressure within the pleural cavity. Pleural cavity is the space found between the chest wall and lungs and is fluid filled. Because the lung is elastic, it can shrink or expand, and when it shrinks, it can become atelectatic. When there is elastic shrinking of the lung, it makes it relax and this arises because of the loss in negative pressure within the pleura. It is common to have loss of pleural negative pressure in conditions like pneumothorax and pleural effusion.
Cicatricial atelectasis
When there is scarring of the lung or fibrosis that reduces the ability of the lung to expand, it may cause a type of bibasilar atelectasis referred to as cicatricial atelectasis. In patients with fibrotic disorders, it is likely that alveoli will be trapped resulting in atelectasis.
Adhesive atelectasis
In the inside of the lungs, there is a surfactant or a liquid that covers it. This liquid reduces tension and allows the alveoli or air sacs to remain open. So when there is surfactant deficiency, it makes the alveoli to collapse resulting in atelectatic state. In patients who have pulmonary embolism, it is likely to have impairment of the surfactant because there is loss of blood flow and lack of carbon dioxide.
Round atelectasis
Also referred to as Blesovsky syndrome, round atelectasis or folded lung occurs when there is trapping of the lung caused by pleural disease. Patients with asbestosis may experience Blesovsky syndrome. Asbestosis is a disease that affects the lungs and is caused when a person inhales asbestos particles. A false mass-like appearance may be seen in this kind of lung collapse.
Discoid atelectasis
With this type of atelectasis, there is partial lung collapsing, and the collapsed section doe not re-inflate properly meaning there is lack of airflow. The commonest reason for having discoid atelectasis is the side effects of anesthesia, which is used during surgery. The atelectasis may also occur in people who have received multiple surgeries.
Right middle lobe syndrome
Also known as chronic right middle lobe collapse, the right middle lobe syndrome is linked to various diseases such as bronchiectasis, pneumonitis, and recurrent atelectasis of the middle lobe.
Symptoms
There may be no noticeable symptoms when you have bibasilar atelectasis, however, if they occur, they may include:1,2,3,4,,6,7,8
- Coughing
- Rapid, shallow breathing
- Shortness of breath
- Fever
- Anxiety
- Sputum
- Reduce chest expansion
- Breathing difficulties
- Wheezing
- Severe pain
- Skin discoloration
Causes
The causes of bibasilar atelectasis are grouped into two categories based on the nature in which the condition occurs. One group is that of obstructive bibasilar atelectasis and the other comprises non-obstruction atelectasis. Obstructive atelectasis is mainly due to blockage of airways while non-obstructive occurs due to pressure emanating from outside the lung.1,2,3,4,5,7,8,9,10
Obstructive Bibasilar Atelectasis
When there is obstruction of airways leading to atelectasis, it may be due to the following:
Foreign object
You may have the lung obstructed when you inhale an allergen that makes the lungs to collapse.
Mucus plug
When an individual undergoes lung surgery, the lungs may respond to the medication by reducing its rate of inflation. This allows mucus to collect within the airways. While doctors may try removing the mucus using suction technique, some may continue to collect. This could result in collapse of the lung. Deep breathing exercises may help a patient to expel the mucus during recovery after a surgery procedure. The mucus plugs may also occur in persons who have cystic fibrosis and asthma.
Blood clots
When blood moves from the bloodstream to enter the interior of the lungs because of a pressure caused by a blood clot, then a person may suffer from bibasilar atelectasis.
Damage to lungs
The walls of the lungs may be damaged by conditions such as pneumonia and COPD making air to move from the lungs and enter the space between the lung and chest wall. This may result in collapse of the lung or bibasilar atelectasis.
Constriction of airway
When there is scarring in the lungs caused by chronic infections such as tuberculosis, fungal infections, or some other lung diseases, it may narrow the airways. The narrowing of airways restricts the air passage resulting is atelectasis. The constriction of airways may also be caused by an abnormal growth.
Non-Obstructive Bibasilar Atelectasis
If obstruction isn’t the cause for atelectasis, pressure may be the culprit and it can be caused by the following:
Trauma
A person may have lung compression if they are hit directly onto the ribs or lungs. This may occur from an auto accident, gunshot, stabbing, or some other accidents. Lung tumor, obesity, lung pressure, and prolonged use of cough suppressants can also contribute to bibasilar atelectasis.
Anesthesia
This is a common cause for atelectasis. During surgery, doctors may use anesthesia to numb the area of operation. Since anesthesia changes the way you breathe and interferes with gas and pressure absorption, it can make the alveoli to collapse resulting in bibasilar atelectasis.
Pleural effusion
Fluid can collect and build up in the space between the area in lining of the lungs and chest wall. This space is the one referred to as the pleura. When this happens, it prevents the lungs from inflating or expanding.
Pneumothorax
When there is air leaking from the lungs to enter the pleura or the space between the chest wall and the lung’s lining, it may result in a condition known as pneumothorax. This may indirectly cause problems with lung inflation and it may result in collapsing of the lungs or atelectasis.
Pneumonia
This is an infection of the lungs caused by microbes like bacteria, fungi, and virus. Due to the infection, the alveoli may fill with fluid or pus and this may cause breathing difficulties. A person having pneumonia may experience temporary non-obstructive atelectasis.
Lung tissue scarring
Things like injury, surgery, or lung disease may contribute to scarring of lung tissue. This could result in atelectasis, however, in this situation the damage caused by scarring is more serious than the atelectasis itself.
Tumor
While a large tumor may be present, it may not necessarily be blocking the airways, however, it can induce pressure on the lungs something that makes it to deflate. This can contribute to bibasilar atelectasis.
Drugs
Certain drugs including sedative drugs or opioids can put an individual at risk of having atelectasis, especially if they are taking them in large amounts3.
Diagnosis
If a doctor suspects that you have bibasilar atelectasis, he or she will perform a physical examination. The doctor will also want to examine your recent medical condition as well as treatments you may have had. The symptoms you experience may also guide in the diagnosis.
Proper diagnosis of bibasilar atelectasis is required to prevent a misdiagnosis. Depending on the symptoms you are having, a doctor will order for further tests to confirm the diagnosis. The tests include:
Chest X-ray
This can help to see any foreign object that may be lodged in the airways.
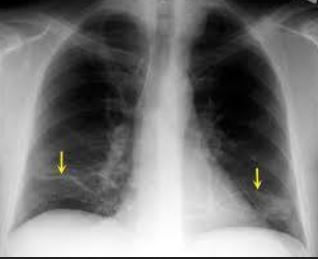
CT scan
Having a computed tomography (CT) scan done on the chest can create pictures that help the doctor to see what is happening. This imaging test tends to show more details when compared to X-ray. It may also help determine if there is tumor that is causing the lung to collapse, something that may not be seen from normal X-ray pictures.
Bronchoscopy
A doctor may use an instrument known as a bronchoscope to look at the inside of the airways. A thin, flexible tube is inserted into the airway, and the tube has a tiny camera and light to allow a doctor to see the interior parts of the airways. If there is blockage in the airways, a doctor can remove them during this procedure for example, a tumor, mucus plug, or some foreign body.
Oximetry
With this test, a doctor will use a device that measures the saturation of oxygen in the blood. The small device is usually placed on your finger.
Treatment
Treating bibasilar atelectasis will largely depend on the causal factor. Sometimes, the atelectasis may go away without needing treatment if it affects only a small area. The presence of an underlying condition causing atelectasis will prompt a doctor to develop the right treatment. For example, if a tumor is the culprit, treatment may involve shrinking or destroying it using surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy.5
Chest physiotherapy
A doctor may suggest that you have chest physiotherapy to help re-expand the collapsed lung tissue. The techniques should also be learned if you are going to have surgery and they include:
- Clapping or percussion within your chest, and it is done over the area that is collapsed to help loosen mucus. There are mucus-clearance devices that may be used to clear the mucus. A good example of the device is the air-pulse vibrator, whether hand-held or a vest.
- Coughing
- Deep breathing exercises may also help. A person may need to use a device that assists him or her to cough deeply.
- Postural drainage, where you position the body to have the head being lower than the chest. This can allow mucus in the bottom of the lungs to drain.
- If you have shortness of breath, supplemental oxygen may be needed.
Bronchoscopy
This minimally invasive procedure uses a flexible tube put down the throat to help clear the airways.
Suctioning mucus
The mucus may be extracted using suctioning forces.
Medication
A patient may be prescribed medication such as Foradil if they have bronchitis. This medicine helps expand the bronchial tubes allowing a patient to breathe easily. To expel mucus, a patient may be administered acetadote to thin the mucus and allow ease of coughing up9.
Reference List
- Bibasilar Atelectasis. https://www.healthline.com/health/bibasilar-atelectasis
- Bibasilar Atelectasis: Types, Symptoms, Risk Factors, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention. https://www.doctorshealthpress.com/general-health-articles/bibasilar-atelectasis/
- Bibasilar atelectasis: Symptoms, causes, and complications. https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/322027.php
- Atelectasis: Causes and Symptoms. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/atelectasis/symptoms-causes/syc-20369684
- Atelectasis: Diagnosis and Treatment. https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/atelectasis/diagnosis-treatment/drc-20369688
- What Is Bibasilar Atelectasis? https://www.findatopdoc.com/Healthy-Living/what-Is-bibasilar-atelectasis
- What Is Bibasilar Atelectasis? https://www.findatopdoc.com/Healthy-Living/bibasilar-atelectasis
- Bibasilar Atelectasis: Causes, Symptoms, Treatment, Diagnosis. https://www.epainassist.com/chest-pain/lungs/bibasilar-atelectasis
- All You Need to Know about Bibasilar Atelectasis. http://www.newhealthguide.org/Bibasilar-Atelectasis.html
- Lung Lobes. http://www.therespiratorysystem.com/glossary/lung-lobes/
