What is Neurapraxia?
Neurapraxia is a condition where the nerves are injured leading to short-term neural dysfunction usually lasting from six to eight weeks till full recovery is attained. During this time both motor functions (control over movement through coordination of muscles) and sensory functions (transitions of sensations such as pain) may be lost. Neurapraxia is considered a mild type of nerve injury.
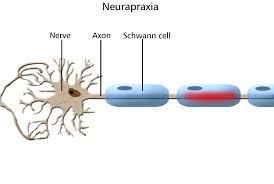
What causes Neurapraxia?
Neurapraxia is caused by several factors that may that lead to blockage of the nerves and therefore prevent transmission of impulses. These factors can either be traumatic (injury resulting from physical harm from an external source) or non-traumatic (injuries that result in physical harm, but from within the body itself).
Traumatic
Some traumatic causes of neurapraxia are:
- Accidents such as car and motor accidents, or those that involve falling from an elevated place resulting in to injury to the nervous system as a result of nerve compression. The nerve injury results in neurapraxia. The neck and spinal column are especially vulnerable during these situations.
- Tissues within the body may swell leading to nerve compression, and this may be occur as a result of being hit by an object or through motor accidents.
- Lacerations or penetration by sharp objects may lead to neurapraxia whereby the nerve is injured both partially or completely
- Injury sustained during a dislocation or fracture may cause stretching of nerves or compression of nerves.
- Injuries sustained from blunt objects may result in nerve damage through contusions whereby the nerves are compressed
- Injuries sustained from gunshots wounds can lead to injury of the nerve either partially or completely
- Compression and blockage of the nerves as a result of blood collecting outside the vessels, a condition referred to as hematoma
- Through violent traction such as in the arm, which puts stress on the nerves
- During child birth, especially a difficult one where the child’s neck muscles and nerves are injured due to stretching, a condition known as brachial plexus neurapraxia.
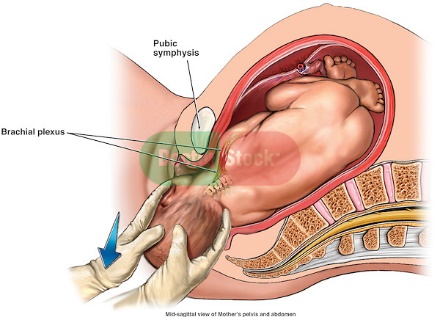
This image illustrates branchial plexus injury during child birth.
Non-traumatic
Non-traumatic causes of neurapraxia include:
- Diabetes can lead to nerve damage, as high blood glucose levels may damage the blood vessels that supply the nerves with nutrients. One in every 4 people diagnosed with diabetes exhibit some form of nerve damage.
- Treatment of cancer through chemotherapy and radiation therapy can lead to nerve damage
- Side effects of some drugs as well as mode of treatment such as taking antiretroviral medication for HIV can lead to nerve damage
- The accidental ingestion of toxic substances such as mercury and lead may also contribute to neurapraxia
- Nutritional deficiency may lead to nerve damage, especially lack of vitamin B6 (for production of brain neuro-transmitters), vitamin B12 (for maintenance of central nervous system function as well as nerve regeneration and repair), and vitamin E (for maintenance of central nervous system function as well as nerve regeneration and repair).
- Some infectious diseases also damage the nerves including HIV, herpes virus, Lyme disease and Hepatitis C virus. Diseases such as Lou Gehrig also result in progressive nerve damage.
- People who suffer from alcoholism may experience significant nerve damage since alcohol can be toxic to the nerves.
Who are Commonly Affected by Neurapraxia?
Neurapraxia is a condition that commonly affects athletes involved in sports that have a lot of collision such as American Football and Professional Wrestling. That is why the NFL outlawed acts such as spearing, lowering an opponent’s head or knocking him with the crown of your helmet, which posed great risk to the cervical spine region causing cervical cord neurapraxia.
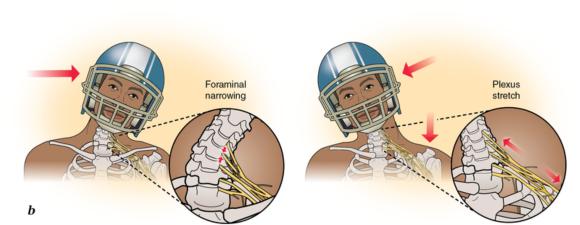
Such injuries are common in the NFL and result in cervical cord neurapraxia. Famous WWE superstar Adam Copeland also known by his stage name “Edge” retires after 13 years in 2001 due to neurapraxia.
Signs and Symptoms of Neurapraxia
The signs and symptoms of neurapraxia include the following:
- Weakening of the muscle
- Paralysis of the muscle
- Complete loss of sensation or abnormal sensations such as numbness usually occurring where the nerve has been damaged
- Pain in the area or region where the nerve has been damaged
- Sweating excessively
- Dysfunctions of the bowel and bladder.
How do you Treat Neurapraxia
Since neurapraxia results in the nerves being impaired for a short period of time, recovery of normal body functions may start within the first two months. In most cases, it recovers after a period of 6 to 8 weeks, but in some instances, it takes longer – up to four months for full restoration.
Even though the recovery period in patients having neurapraxia may vary, the mode of recovery is usually fast and complete. Here are a few methods of how to treat neurapraxia?
Diabetes
Where the cause of neurapraxia is diabetes, medication should be taken to keep the sugar levels in check, a proper diet may also help in maintaining proper sugar levels
Nutritional deficiency
A proper diet is advised, taking a lot of fruits is also recommended as well as taking vitamin supplements
Change of Drugs
In cases where neurapraxia is as a result of side effects from medication drugs, the medicine may be replaced with those that don’t cause any side effects or with a more mild form of medicines
Surgery
Whatever structure is compressing the nerves and causing neurapraxia, for example, blood clot, or blood collecting outside a blood vessel can be removed surgically
AutoImmune Conditions
Where neurapraxia is caused by autoimmune conditions, medication can be taken to keep the body’s immune system in check
Physical therapy
Physical therapy is also recommended for the healthy recovery from different nerve injuries.
Although neurapraxia may be a temporary condition that takes a short time to heal, usually from six months to a maximum of eight months, if left untreated or if treatment is not administered correctly, the condition may turn out to be more severe and in some cases permanent.
It is important to know that having repetitive neurapraxia within the same region like it happens in sportspersons taking sports such as wrestling and football, even after treatment, it may lead to permanent damage to the nerves.
Reference list:
- http://heydoctor.org/neuropraxia.html .
- http://www.en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/neurapraxia .
- http://www.healthtype.com/nerve-injury-neuropraxia-axonotmesis-neurotmesis-and-healing.html .
- http://www.wheelessonline.com/ortho/nerve_injury
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000714.htm
- http://www.webmd.com/diabetes/nerve-damage-diabetes#2-4
- https://www.drugs.com/cg/neurapraxia.html
- https://www.livestrong.com/article/508599-nutriton-for-nerve-regeneration

One comment