What is Monomorphic Ventricular Tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia is a rhythm that beats faster than 120 beats per minute. The rhythm can come from distal conduction system, ventricular myocardium or both of them3.
Ventricular tachycardia is common in developed countries but less common in developing countries. Ventricular tachycardia affects patients with congenital heart disease but uncommon in children. Ventricular tachycardia affects mostly men because they are at risk of coronary heart disease or ischemic heart disease.
Forms of Ventricular tachycardia
Ventricular tachycardia is classified according to the appearance of the rhythm on the electrocardiographram. The following are the forms of ventricular tachycardia1, 2:
Monomorphic Ventricular tachycardia
This rhythm occurs when the QRS complex is the same in all the beats and it originates from one source.
Polymorphic
This is a type of ventricular tachycardia where the QRS complex varies from one beat to another and the beats comes from different sources.
Causes
There are several causes of ventricular tachycardia such as2, 4
Ischemic heart disease
This is a disease that disrupts the supply of blood to the heart. It is also called coronary heart disease. This disease causes your arteries to become narrow as a result of deposits of cholesterol and fats. This decreases the supply of nutrients and oxygen to your heart muscles which are needed for their proper working. This will eventually deprive off the affected section of your heart vital nutrients and oxygen causing death in the region of your heart and can lead to heart attack.
Ischemic heart disease occurs as a result of high blood pressure, high cholesterol in the blood and diabetes. Stress is another cause of this condition.
Dilated cardiomyopathy
This is condition that causes your heart muscles to become thin and stretched. This affects the ability of your heart muscles to pump blood around the body.5
Dilated cardiomyopathy is caused by factors such as high blood pressure, smoking, excessive intake of alcohol and viral infections. This condition can arise from genetic factors. Changes in the genes causing this disease can be passed from the parent to the child.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
This disease occurs when your heart muscle cells expand and cause the walls of the left ventricles to become thick. The thickening can obstruct blood from flowing properly out of the ventricles as well raise blood pressure which can cause abnormal heart beats.
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is an inherited condition. It occurs as a result of changes in the genes of heart muscle proteins. Diseases such as diabetes and thyroid disorders can cause hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.
Electrolyte deficiencies
Electrolytes are vital in the body because they help conduct electrical signals. Sufficient level of calcium, potassium and magnesium help boost the electrical signal between your heart muscles which enables enough blood to be pumped around the body. In case there is a drop in the levels of any of these electrolytes, electrical signal between your heart muscles becomes poor which decreases the amount of blood pumped around your body.
A low level of magnesium in your body is called hypomagnesemia.
Systemic disease
Systemic disorders can also cause ventricular tachycardia. Autoimmune disorders such as lupus can attack and destroy myocardium of your heart. This can raise blood pressure in your ventricles which can lead to faster heart beat.
Medications
Certain drugs can cause your heart to beat faster. Drugs that extend QT interval such as class III antiarrhythmics and levofloxacin can cause ventricular tachycardia. Other drugs such as halothane that decrease the conduction velocity may also cause your heart to beat faster.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis of monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is done through the following3:
Electrocardiogram
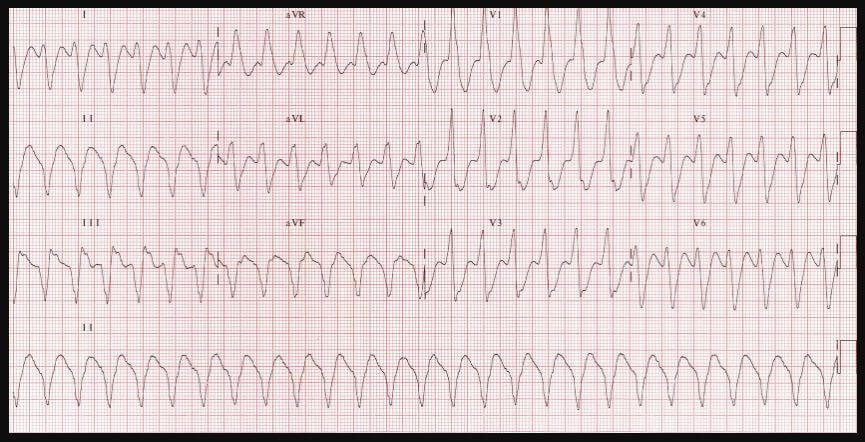
This is a test done to check if you have a heart disease. This test records electrical activity of your heart muscles through an electrode that is attached on the skin of your legs, arms or chest. Through electrocardiogram test, your doctor can look for abnormalities in your heart such as thickened artery walls, check for your heart rhythm and flow of blood in your heart.
Prior to this test, you should avoid lotions and creams on your skin the day of the test. These creams may prevent the electrodes from making contact with your skin. There are several electrocardiogram tests that your doctor can suggest such as:
Holter monitor
This test is used to check your heart for 24 or 48 hours. Your doctor may recommend this test if you have palpitations, have insufficient flow of blood to your heart muscles or abnormal heart rhythm.
Event monitor
This test is ordered if you experience regular symptoms of heart diseases. You will wear this device which you press a button to record the electrical activity of your heart muscles. You may put on this device for several weeks or months. When you record your heart’s electrical activity, the information is sent to your doctor’s phone.
Treatment
Treatment for ventricular tachycardia depends on the stability of the patient and the underlying cause. The main aim of treatment is to stabilize the patient’s heart rhythm. Patients with monomorphic ventricular tachycardia can be treated with following treatment options:1
Synchronized direct current (DC) cardioversion
This treatment is for unstable patients with monomorphic ventricular tachycardia. It involves an energy dose of 100J monophasic.
Intravenous (IV) procainamide or sotalol
It is given to stable patients with a normal left ventricular function to restore the normal sinuses rhythm. Beside sotalol, your doctor can also use lidocaine. Patients with a weak left ventricular function are treated with intravenous lidocaine or amiodarone.
Patients suffering from heart failure are treated using the following:
- Bet receptors such as bisoprolol, carvedilol and metoprolo.
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
Statin therapy
This therapy is useful for patients with coronary heart disease. It is used to lower the risk of abrupt cardiac death, vascular accidents and ventricular arrhythmias.
Medicines
Your doctor may recommend certain drugs to help lower your high blood pressure and control the unusual heart rhythm.
Diet
Eating a healthy diet can help reduce the risk of most heart diseases. Eat a diet with low cholesterol and low salt to lower high blood pressure. Avoid caffeine and other stimulants. Quit smoking because cigarette increases your risk of cardiovascular complications.
In case of electrolyte imbalances, your doctor will come up with strategies to restore their level in your body. Your doctor may recommend food rich in magnesium or calcium or use of supplements.
Reference list
- https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/159075-treatment#d14
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2672286/
- https://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Monomorphic+ventricular+tachycardia
- Ischemic Heart Disease. http://www.srspharma.com/ischemic-heart-disease-treatment-causes-symptoms.htm
- Dilated cardiomyopathy. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/dilated-cardiomyopathy
- https://lifeinthefastlane.com/ecg-library/ventricular-tachycardia
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ventricular_tachycardia
- circ.ahajournals.org/content/92/3/421
- emedicine.medscape.com/article/159075-treatment
- https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ventricular-tachycardia
- bestpractice.bmj.com/topics/en-us/537
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0736467916307211
- https://books.google.co.in/books?isbn=0792365593
