What is Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever?
The abbreviated term for Rocky Mountain spotted fever is RMSF, it’s a tickborne disease or bacterial disease that is spread to an individual from a bite of a tick infected with the causal bacterial. People who suffer from RMSF have symptoms such as headache, fever, and rash. If a patient does not get treatment in time, the disease can be deadly1.
It can cause damage to a patient’s internal organs including the heart and the kidneys. The disease was first reported in the Rocky Mountains areas, it is now commonly seen in the U.S.’s southeastern areas. The disease has also been reported in other areas including South America, Central America, Canada, and Mexico2.
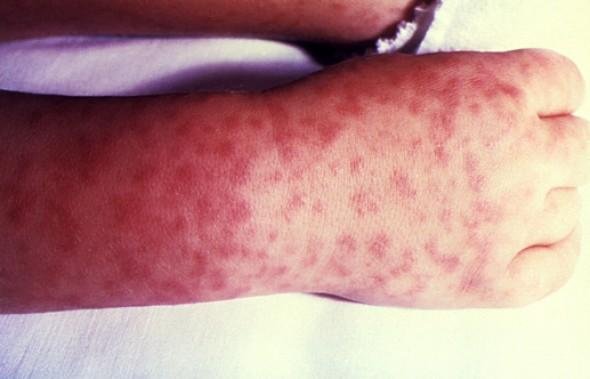
RMSF affects blood vessel lining causing damage that may occur in all organs. Blood tends to leak from the vessels and that is why internal organs are affected.
Causes of RMSF
The disease is caused by a type of bacteria referred to as the spotted fever group rickettsia. Other likely causes of the disease are R. parkeri that causes Rickettsia parkeri rickettsiosis and Rickettsia akari that causes Rickettsialpox.
The Rickettsia philipii causes Pacific Coast tick fever, which is also part of the rickettsioses group of spotted fever.1
Transmission
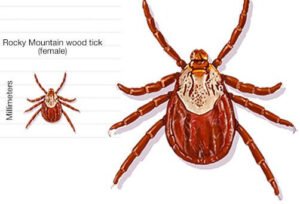
A person will have Rocky Mountain spotted fever when they are bitten by a tick that carries the causative agent Rickettsia rickettsii. The ticks that carry this type of bacteria are known to be the commonest cause of the disease.
When an infected tick bites your skin and sucks blood for a period of about six to 10 hours, it is likely that you will pick the disease. In most cases, you may never see that tick biting you. The spotted fever occurs in times when ticks are active. It may also be common during warm weather when individuals spend their time outdoors. It’s not possible to contract the disease from another person- it cannot be spread between persons.
Symptoms of Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever
Many people who have been infected with the bacteria will become ill in their first week of infection. However, the symptoms may delay and appear in about 14 days. During the initial stages, the symptoms tend to mimic other illnesses and may not be specific. A patient will have symptoms such as:
- Muscle aches
- Chills
- High fever
- Severe headache
- Neurological changes including confusion
- Vomiting and nausea
- Poor appetite
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain.
A distinctive rash occurs in individuals who have the infection. An individual will have a red, non-itchy rash that appears in about 3 to 5 days following the initial symptoms and signs as mentioned above. The first appearance of the rash are noticed in the ankles and wrists.
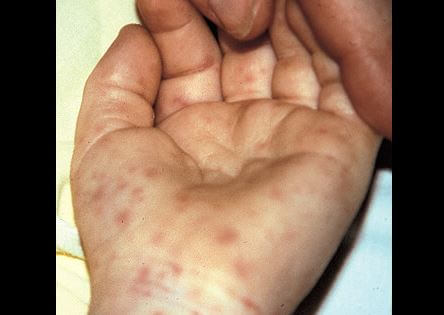
The rash can spread in either directions, for instance, it can move down to your palms or spread to the feet’s soles. It can also move up the arms and the legs to the torso. One thing that can make diagnosis of the disease a big problem is because some people don’t develop the rash.
A second rash may develop after the sixth day and it tends to appear purple-red. When this kind of rash develops, it’s an indication that the disease has become serious. Treatment should be done before this stage of rash. The rash itself is regarded the classic symptom, however, about 10 to 15 percent of individuals having the disease don’t develop any rash at all. Also, only about half of individuals who suffer from RMSF can remember having noticed a tick bite. 5
Diagnosis of RMSF
It may be difficult to diagnose a patient of this disease because it’s early symptoms and signs tend to be similar to symptoms of other diseases or health conditions like flu.
- A doctor will have physical examination to see if the rash has developed
- Laboratory tests may be ordered to check blood samples of the causal bacteria. The doctor may order rash specimens to be tested in the laboratory.
- If the patient can provide the tick itself, it can provide evidence to help confirm that the symptoms are related to the organism. Usually, doctors don’t wait for the test results since it is important a patient gets antibiotics in a timely manner, so treatment may begin when there is a strong evidence suggesting that the symptoms and signs are associated with the causative agent.
- Specialized laboratory tests may continue to be conducted such as latex agglutination, immunofluorescent antibody tests, or enzyme immunoassays to help confirm the disease. These tests can take weeks and will be done when the treatment is ongoing.
During infection with the bacteria and upon development of RMSF, a patient may develop antibodies developing on their immune system. This occurs within the first 7 to 10 days following the onset of the illness. What this means is that the specialized confirmatory tests such as immunofluorescent antibody tests may turn negative during the initial week. However, doctors will order for indirect immunofluorescent assay to see if there is rise in antibody titers.6
Treatment of RMSF
People who have Rocky Mountain spotted fever will most likely prevent complications if they get treatment within five days after they showed symptoms. Doctors will already have started treatment using antibiotics even before the test results are received just to ensure the disease is contained. The most effective antibiotic therapy is use of: 2,3,4,5,6
- Doxycycline or Monodox and Vibramycin
- chloramphenicol
Doxycycline medication however may not be recommended to pregnant women. A doctor may thus prescribe chloramphenicol if you are pregnant.
The CDC has recommended that a patient start using the antibiotic immediately he or she has been diagnosed and suspected of having Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Delay in treatment can lead to serious complications. The patient should take the medication exactly has it has been prescribed by a doctor.
Long term Effects
When not treated in time and in the right way, Rocky Mountain spotted fever could cause damage to body. It may damage the lining of the blood vessels, organs, and tissues. Some of the complications include:5,6
- Kidney failure because small blood vessels feeding blood to the kidneys are damaged
- It can lead to gangrene (referring to dead tissues in toes and fingers) because of damage caused to blood vessels that supply blood to the toes and fingers. There is disruption of blood flow to the extremities. As a result, amputation may be called for in a patient.
- Meningitis may occur because of inflammation of the brain something that leads to things like seizures and coma
- It can lead to liver and spleen enlargement
- Could cause lung inflammation
- Can lead to heart inflammation or myocarditis
- Damage to eyes because of inflammation occurring on vascular structures feeding the eye
- If not treated, death may occur.
In case a patient has a severe form of RMSF, it may result in other health problems that could be long term including:
- Deafness or loss of hearing
- Neurological deficits
- Muscle weakness
- Paralysis of body occurring on one side.
Reference List
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF). Available at https://www.cdc.gov/rmsf/index.html
- Rocky Mountain spotted fever. Available at https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/rocky-mountain-spotted-fever/symptoms-causes/syc-20361032
- Everything You Need to Know About Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. Available at https://www.healthline.com/health/rocky-mountain-spotted-fever#modal-close
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (RMSF). Available at https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/228042-overview
- Everything You Need to Know About Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. Available at https://www.healthline.com/health/rocky-mountain-spotted-fever#modal-close
- Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever. Available at https://www.medicinenet.com/rocky_mountain_spotted_fever_rmsf/article.htm
