What is Herpangina?
Herpangina is an illness caused by the Coxsackie virus type A. This same variety also causes the hand, foot and mouth disease. The Coxsackie virus was first discovered in the town Coxsackie hence its name. It mainly affects children especially during summer time, adults are not susceptible to get herpangina.
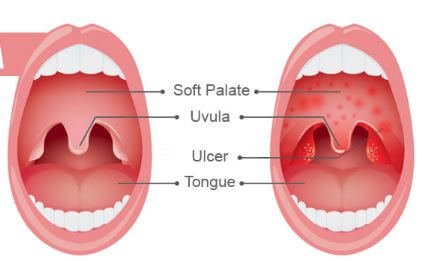
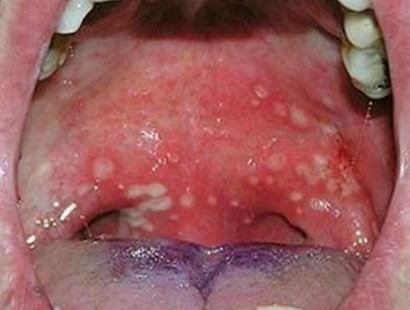
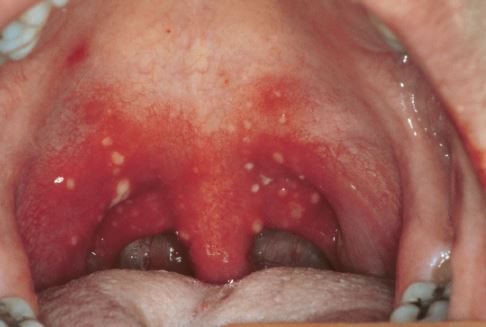
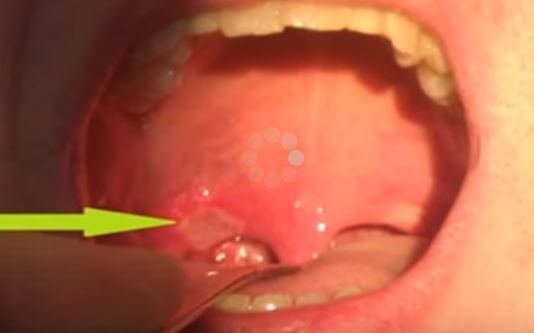
Children affected by the illness often complain of fever and mouth sores. They develop symptoms of sore throat and show signs of a high fever. They are also prone to develop blisters at the palate and the back of the throat. This in turn may cause difficulty in ingesting food stuff, thus they may decline to take any food or drinks and this may cause them have dehydration.
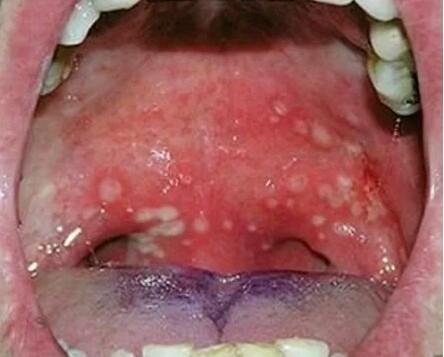
Causes
The main cause of herpangina is directly linked to the Coxsackie A viruses, though other enteroviruses have been linked too. These viruses are composed of one strand of ribonucleic acid and can also be referred to as picornaviruses which means small viruses. Patients should understand that in most cases, Coxsackie viruses are not serious. They cause only mild symptoms and in most scenarios they resolve in a week’s time.
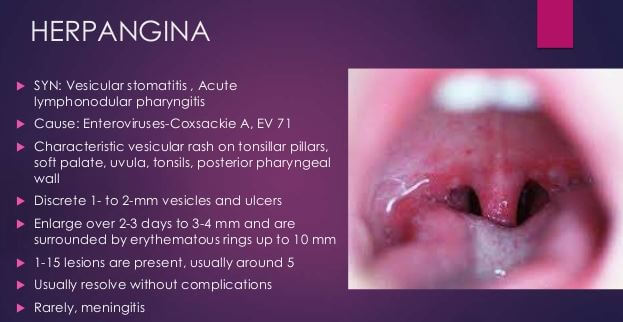
The viruses are spread through sneezing or coughing or through contact of either hand or any other organ with fecal matter. Most individuals infected with these enteroviruses do not display any symptoms making prevention of their transmission very difficult.
Herpangina is very contagious and is easily transmitted from one child to another through unwashed hands, coughing, sneezing or contaminated surfaces. In most instances, people infected with the virus are most contagious during the first week of illness. Infections in body have an incubation period and in the case of herpangina, this involves an asymptomatic period that lasts between one to two weeks.
Symptoms
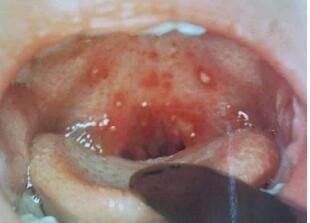
On normal instances children with herpangina have the following signs and symptoms:
- fever closely accompanied by sore throat
- difficulty in ingesting food and drinks
- ulcers in the mouth, soft palate, pharynx, tonsils and uvula
- enlarged lymph nodes is another sign
- also the presence of a rash, which may or may not appear.
Children may also experience headaches, joint pains and inapptences as other signs of herpangina. It is important to point out that these signs and symptoms vary from one person to another. Caution should be taken if symptoms of dehyrdration start to show or a fever that is over 106F and that refuses to go away. You should immediately contact a doctor.
Diagnosis
Herpangina is basically a clinical diagnosis. The ulcers that form as a result of herpangina are one of a kind ( tend to be grey and have a red border), doctors can diagnose the illness by a physical exam. Therefore, subjection to any laboratory tests is not required but if you desire to have the antibodies to the Coxsackie virus measured you can request so but it is highly unnecessary.
Treatment
The main agenda of treatment is to manage and reduce symptoms, thus an individual’s treatment plan will depend on various factors like tolerance of medication, any allergies, age and symptoms among other things.(2,3,4,5)
Use of drugs
Herpangina is a virally induced illness thus antibiotics will not be effective for the treatment. The treatment issued is supportive just like for most viruses. Ibuprofen and acetaminophen may be administered by your physician to ease fever and help in pain control. It should be noted that persons under the age of 20 should not be given aspirin as it is known to be a cause of the Reyes illness. Topical anesthetics like lidocaine give relief to any mouth pain associated with herpangina and sore throats.
Adequate rest
Ensure your child gets plenty of rest and keep them indoors as long as they have a fever.
Take fluids
Increase the intake of fluids in your child’s diet, warm fluids may ease throat pain and fluids like yoghurt soothe the throat. Be sure to avoid hot drinks or citrus based beverages as they may make the symptoms worse.
One ingenious home remedy to soothe blister pain is to treat the blister directly with saltwater. Add four tablespoons of salt to water and gaggle it for a minute a few times a day. Salt is known to help wounds heal and posses antiseptic properties.
It is important that all medicine or drugs administered to treat herpangina should be issued by a certified physician, do not attempt to self-medicate yourself as it may cause adverse effects.
Prevention
Observe good hygiene
Herpangina can be prevented by practicing good hygiene. Ensure that you and your child’s hands are washed thoroughly after using the restroom or after changing a diaper, also before and after partaking in a meal.
Cover your mouth
Practice proper etiquette by covering your mouth or nose while you sneeze or cough. Clean any toys or surfaces around your children thoroughly with a disinfectant to kill germs.
It is important to keep your children from daycares or from contact with a person infected with Coxsackie virus. This is however difficult since most people infected do not display any symptoms. It should be noted that herpangina has no vaccine.
Most children who contract herpangina make a full recover within the period of seven to ten days, but as a wiseman once said prevention is better that cure, ensure you contact a doctor incase of any uncertainty or any severe symptoms and be keen to follow the doctor’s instruction to the latter. This will ensure that your child makes a quick recovery and they will be back to their normal burst of good health and wellbeing in no time.
Herpangina vs. Foot and mouth Disease
Herpangina is also similar to the hand foot and mouth disease but their symptoms vary. In the symptoms of hand foot and mouth there is the development of a rash on the palms but in herpangina there is no rash. 5
It is important to take great caution and protect your children from contracting the illness. In some cases, the illness is not harmful, but in other cases, it may be severe and could lead to meningitis.
Pictures
Reference List
- Herpangina in Children – http://www.childrenshospital.org/conditions-and-treatments/conditions/herpangina
- Herpangina http://www.nytimes.com/health/guides/disease/herpangina/overview.html
- Herpangina https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Herpangina
- http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/218502-overview
- Herpangina http://www.healthline.com/health/herpangina
