What Is Steatorrhea?
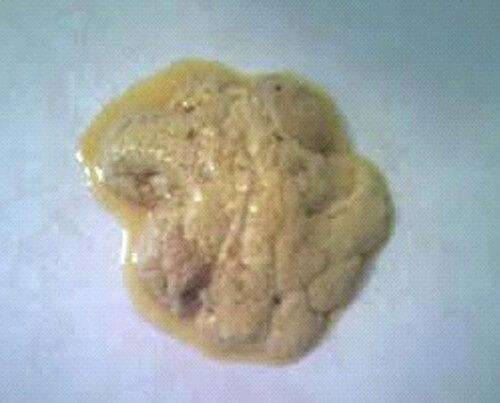
Steatorrhea is not really a medical condition but a syndrome of malabsorption characterized by high fat content in the fecal matter which is foamy (has an oily or greasy appearance), bulky and floats, and with a foul smell which is because of the high fat content in the fecal matter
When the human body fails to absorb fats through the intestines (the small intestines), the body eliminates them from the stool.

Causes
Steatorrhea is caused by:
1. Diseases affecting the liver
Diseases that cause a deficiency in conjugated bile salts (which are crucial for digestion of fats) such as hepatitis, primary biliary cirrhosis and extrahepatic biliary obstruction lead to malabsorption of fats causing steatorrhea.
Taking of excessive alcohol can also make you susceptible to alcoholic liver disease, which can damage the liver and impair its normal functions and therefore lead to steatorrhea.
2. Short Bowel Syndrome
Short bowel syndrome is usually associated with the surgical removal of a significant portion of the small intestines (the removal of the ileum), resulting in a large portion of the small intestines not serving in its duty of absorbing fats leading to steatorrhea.
Reasons for surgical removal of a portion of the intestine include Crohn disease, tumors in the intestine, blood clots and Ischemia (which affect blood flow to the intestine leading to damage), direct injury to the intestines or complications during child birth i.e.
Gastroschisis (when intestines develop outside the body before birth), necrotizing enterocolitis (inflammation of the intestine and loss of blood flow leading to damage to the intestine) etc. 4

3. Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is caused by gastrinoma, which is basically a tumor occurring on the pancreas or the duodenum. It then causes excess production of acid (hydrochloric acid) in the stomach.
When pancreatic enzymes such as Lipase that is responsible for digesting fats and lipids, when this enzymes are exposed to this acid they become inactive leading to less absorption of fats and causing steatorrhea.
4. Intestinal Stasis
Intestinal stasis can be caused by diabetes or scleroderma. Which means food content in the intestine is not being pushed properly through peristalsis, and bacteria may develop Such bacteria metabolize bile acids early in the small intestine instead of this happening in the large intestine and therefore affecting digestion and absorption of fats causing steatorrhea.
5. Parasitic Infections
Parasitic infections such as giardiasis, isosporiasis and strongyloidiasis are caused by parasites that damage the brush borders of the intestinal lining and therefore inhibiting fat absorption. In cases where the cause of the steatorrhea is unexplained, giardiasis should be considered as the giardia lamblia parasite has either destroyed the intestinal mucosa or deconjugates the bile acids early.
6. Some drugs and food intake
Some drugs and food cause steatorrhea. Taking of excess whole nuts can lead to fat in the stool as lipids in whole nuts is less properly absorbed as compared to their nut butters, oils or flour. Medication also cause steatorrhea by inhabiting the absorption of fats within the body, such drugs include Orlistat (a diet pill), Vyotrin is said to cause steatorrhea among some people, Para-aminosalic acid (antibiotic used to treat Tuberculosis), Colchine (used in treating gout and heavy doses can cause gastro-intestinal upsets), Tetracycline and Neomycin, laxatives as well as weight loss drugs. 5
Symptoms
Indicators for steatorrhea are:
- Stool that is bulky or large
- Stool that is foul smelling
- Stool that is pale in color
- Stool that looks greasy or oily
- Stool that floats on water due to the high fat content
- Quick weight loss usually in months
- Abdominal pain
- Flatulence and rumbling sound in the stomach.
Treatment
The following methods are among some which are used to treat steatorrhea:
- By limiting the fat intake in the diet.
- Reducing the levels of alcohol intake where alcohol is causing liver damage and leading to steatorrhea. Where possible taking alcohol can be stopped completely.
- Taking supplementary pancreatic enzymes (contains pancreatic lipase) together with your meals where it is not possible to restrict fats in the diet.
- Where chronic pancreatitis is the cause of steatorrhea, fat soluble vitamins (vitamins A, D, E and K) are supplemented.
- Where short bowel syndrome occurs recently after surgical removal of a portion of the intestine and therefore causing steatorrhea, then medications such as Teduglutide (promotes mucosal growth and restores gastric emptying and secretion as well) can be administered.
- In some cases, intestinal adaption may take place where the intestine may grow in size, the mucosa may grow thicker, and the villi grows longer and denser to in order to compensate for the portion, which was removed. This restores the intestinal functions to normal.
- Where fat soluble vitamins are ineffective, steatorrhea persists, and there is significant weight loss, then medium chain triglycerides are supplemented to give the body fat-derived calories.
- Where steatorrhea is caused by bacterial outgrowth, antibiotics are administered.
- Where steatorrhea is caused by bile acid malabsorption, then bile acid sequesters (such as Cholestyramine) can be administered.
- Where steatorrhea is caused by Celiac disease, folic acid therapy can be used to treat the condition. Taking of foods rich in folic acid kale, spinach and broccoli is also recommended.
- Where acid (hydrochloric acid) in the stomach causes steatorrhea antacids can be administered to lower acid levels (heightened acid levels mostly seen in short bowel syndrome).
Conclusion
Steatorrhea is not a medical condition but a symptom of some underlying medical condition- it can also be harmless such as when taking of whole nuts is considered a cause. To filter out harmless occurrences diagnosis of steatorrhea is done in 72 hours, here fecal samples are delivered per day for 3 days for analysis.
Steatorrhea has several symptoms but most of the signs of steatorrhea can be identified within the fecal content. Most times the cause of the steatorrhea can be traced, however sometimes the cause can be hidden (idiopathic).
Regular medical checkup however can help in early detection of the cause of steatorrhea. A proper diet as well as exercising also reduced the occurrence of steatorrhea.
References List
- http://www.ihealthblogger.com/what-is-steatorrhea-symptoms-causes-and-treatment/
- https://medicalfoxx.com/steatorrhea.html
- http://healthfixit.com/steatorrhea/
- http://my.clevelandclinic.org/childrens-hospital/health-info/diseases-conditions/hic-short-bowel-syndrome-in-children
- http://www.primehealthchannel.com/steatorrhea-pictures-definition-symptoms-causes-and-treatment.html
- http://healthzene.com/steatorrhea-pictures-causes-symptoms-treatment/
