What is Capnography?
Capnography is an instrument used to measure the amount of carbon dioxide in exhaled air and represents the readings in a waveform tracing. These are vital monitoring devices found in wards, ambulances, operating rooms and intensive and critical care1.

We all know that oxygen is vital for life. Oxygen goes through several steps in your body before it reaches the body cells. Once you breathe in oxygen, it is taken by your body cells which utilizes it and releases carbon dioxide as unwanted product. Carbon dioxide also goes through several steps before it is removed out of the body.
Capnography provides measurement that can help detect if there are problems in your body.
How it Works?
Capnography uses infrared waves to measure carbon dioxide. Infrared waves have a lower frequency compared to light and it is not visible to the naked eye. Infrared is absorbed by gases that have at least two different atoms. Since oxygen has two similar atoms, therefore it cannot absorb infrared waves. Carbon dioxide has two different atoms, thus it can absorb infrared waves.5
Beside carbon dioxide, infrared can measure other gases such as isoflurane and nitrous oxide. Advances in infrared technology has made it easy to reduce the response time and boost its accuracy and create high quality capnography waveforms in untimely babies with faster respiratory rates and small tidal volumes. Carbon dioxide values are shown as partial pressure.
Types of Sensors
Infrared technology consists of two sensors named according to the area where the capnograhy is placed. The following are types of sensors3:
Mainstream sensors
In this kind of sensor, the adapter is put in between the breathing circuit and tracheal tube. Carbon dioxide is then measured across your air passage.
Side stream sensors
In side stream sensors, a sampling tube and an adaptor are used to aspirate the gases from your respiratory system. These gases are then transported to the infrared sensor. The transport of carbon dioxide to the infrared sensor is slow and it results in delay of measuring carbon dioxide and display of the capnography values.
Capnography Measurement
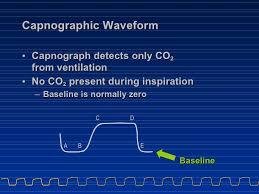
Carbon dioxide waveforms are represented on a graph. It is plotted against time waveforms or volumetric capnography. Time capnography is used in medical practice. Time capnography is divided into two vital sections: expiratory and inspiratory.
The expiratory section is further split into an occasional phase IV and three phases. This is done according to the carbon dioxide released from the airways and lungs of the patient.4
Uses of Capnography
Capnography measurements are useful in terms of health management. The following are some of its uses1, 4, 5:
It helps detect shock
Capnography has circulatory and ventilator features. Your body cells utilize glucose and oxygen to produce energy, and release carbon dioxide into the blood which is transported to the lungs. The quantity of carbon dioxide depends on sufficiency of circulation to your lungs. This offers some details about the circulation of gases around your body.
In case of a low end-tidal carbon dioxide and other symptoms of shock, it shows that you have a poor system perfusion which may occur as a result of sepsis or hypovolemia.
If you experience a cardiac arrest, it means that there is no metabolism and circulation. This results in no production of carbon dioxide. Carbon dioxide can only be produced if your chest is compressed properly. Capnography will give details about compression and whether a change in compressor is required. An end- tidal carbon dioxide value below 10mmHg shows that the compressions are not quick.
Instant feedback on the working of the treatment
Patients with a pulse problem are managed with a bag valve mask to provide pressure ventilation. But using the bag valve mask is not effective in tracking how the bag is squeezed and the amount of air that reaches your lings. By using capnography in pulse patients, the doctor is able to see the waveform which records every squeeze and the quantity of air that enters the lungs.
Capnography is used to guide how quickly to ventilate a patient. In addition to this, capnography is used to correctly place a device in your airways. Capnography is used to evaluate ventilation. Ventilation refers to the movement of air out and in your lungs. Oxygenation is the quantity of oxygen you breathe in the lungs that reaches the bloodstream.
In addition to assessing ventilation, capnography is also used to determine respiratory rate. In healthy people, the brain usually responds to changes in carbon dioxide so as to regulate ventilation. As a patient’s carbon dioxide increases, the respiratory rate also raises and vice versa.
In case the patient has a slow respirations and a high end-tidal carbon dioxide, it shows that the patient’s ventilation is not removing carbon dioxide effectively.
It helps diagnose respiratory problems
Diagnosing respiratory problems may be difficult and wrong diagnosis can be harmful to the patient. Numerous conditions can affect your respiratory system. Adding capnography to physical examination can help the doctor make appropriate decision to treat the underlying cause.
It is used in procedural sedation
Many medical procedures are conducted when the patient is under sedation and monitored by a competent health professional. Patients are normally hurt during sedation. Patients treated using this procedure may have complications such as oxygen saturation and apnea. Apnea is a condition where your breathing is interrupted during sleep. The use of capnography in these procedures has led to decrease in the complications patients may experience.
It is used in intensive care unit
Capnography can be used to monitor ventilation in patients in intensive care unit. Capnography is used to ensure that endotracheal tubes are placed correctly and detect wrongly placed ones.
Capnography can also be used to monitor patients transported to and from intensive care units. It monitors carbon dioxide in patients during transport which ensures that their airways are well ventilated.
Capnography is also used to monitor postoperative patients that need narcotic pain drugs. Patients receiving continuous infusion are at risk of depression which can cause death. Capnography is used to detect early depressions in these patients and provide warnings to the doctor so that steps are taken to manage it.
Reference list
- Capnography – https://www.ems1.com/ems-products/Capnography/articles/2163495-5-things-to-know-about-capnography/
- Capnography. https://www.howequipmentworks.com/capnography/
- Capnography. https://wikem.org/wiki/Capnography
- https://www.apsf.org/newsletters/html/2016/Oct/05_Capnography.htm
- Capnography. http://anesthesiology.pubs.asahq.org/article.aspx?articleid=2034665
