What is Epigastric Pain?
Epigastric Pain or discomfort occurring below the ribs in the upper abdomen. Epigatric pain usually occurs along with other symptoms of the digestive system such as gas and bloating. Many things may cause this kind of pain, so you need to know what the cause may be. It’s also important to differentiate between epigastric pain that is due to something harmless such as lactose intolerance or overeating, and pain which is as a result of an underlying disease or infection or inflammation. 1,2,3,4
Epigastric pain tends to be felt in the area within the middle part of upper abdomen, specially between the belly button and the ribs. It may range from mild to severe and it could spread to other parts of body. Epigastric pain, while it may not be a cause for alarm, if it is occurring persistently or it’s so severe, it may be arising due to some other underlying serious health problems, which need to be checked by a doctor.3
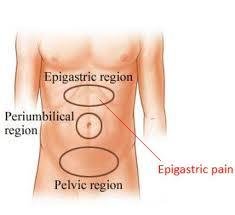
Causes of Epigastric Pain
It is common to have epigastric pain when eating or soon after you have taken your meal. The pain may result in mild discomfort or even extremely painful burning sensation. The following are some of the possible causes of epigatric pain: 1,2,3,4
Acid Reflux
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) and acid reflux may bring about stomach acid, which flows upwards to reach the esophagus. The esophagus is the tube connecting the stomach and the throat. When stomach acid gets to the esophagus, it can bring about epigastric pain. This may happen when you lay down after you have taken a meal. Anyone may experience acid reflux occasionally, but GERD tends to be a chronic disease that should be treated in time.
Heartburn and indigestion
Just like acid reflux, indigestion can occur if the stomach releases too much acid into the esophagus. You may have a heartburn, which brings a burning sensation in the chest. This can also cause epigastric pain. You may have indigestion consistently or it may be temporary.
Gastritis
This refers to inflammation of stomach lining. The condition can be temporary when it’s caused by infections, or it could be chronic.
Pregnancy
When a woman is pregnant, she may have other many health issues including epigastric pain. Since pregnancy brings about increased pressure within the abdominal wall, it could result in pain. Sometimes, when there is fluctuation in hormones, they could cause problems with digestion, which can result in acid reflux that in turn causes epigastric pain. If you have epigastric pain during pregnancy, it can be a symptom of a serious condition like preeclampsia and this requires close monitoring since it can be life threatening.
Taking alcohol
You may not be aware that alcohol can cause epigastric pain, but that is correct. When alcohol irritates or causes damage to stomach lining, it can lead to inflammation that causes pain.
Lactose intolerance
People who have lactose intolerance are unable to adequately digest lactose. Lactose is found in foods such as dairy products. A symptom often seen in people with lactose intolerance is epigatric pain. This pain may also be triggered by other food allergies and sensitivities.
Overeating
When you take too much food, it may put pressure on the abdominal wall resulting in pain. This happens the way pregnancy brings about epigatric pain. Too much eating may also cause indigestion and acid reflux problems thus contributing to the pain. People with eating disorders like binge eating or those who have repeated vomiting once they have eaten food may experience epigatric pain.
Esophagitis
This occurs when the esophagus lining suffers an inflammation. Esophagitis may be caused by acid backup from the stomach, an infection, allergies, or having chronic irritation due to taking of some medications. When not treated, esophagitis could result in scarring of the esophagus lining. The inflammation as well as backing up of acid from stomach may cause epigastric pain.
Peptic ulcer
This is a disease caused by bacterial infection or taking certain medications like nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs used to relief pain. Peptic ulcer disease could cause epigastric pain.
Gallstones or gallbladder inflammation
You may experience epigastric pain if the gallbladder is inflamed or you have gallstones. This condition may be referred to as cholecystitis and it can be so painful often requiring one to be hospitalized or have a surgery.
Symptoms Accompanying Epigastric Pain
If you are experiencing epigastric pain, you may also have other symptoms and they depend on the cause of the pain. These signs and symptoms may include: 2,3
- Nausea
- Bloating
- Vomiting
- Diarrhea
- Constipation
- Weight loss
- Loss of appetite
- Feeling full as you begin to take food
- Hoarse voice or sore throat
- Pain when eating or pain that subsides when you take food or when you have bowel movements
- Pain that is relieved or worsened by movement or when you are in a certain position.
You also want to note that epigastric pain may not only be limited to the area on your upper abdomen, it may radiate to reach other areas like the back, neck, or chest. So, if you get excessive pain occurring in the entire upper part of the body, it could be as a result of acid reflux or gastritis.
Diagnosis of Epigastric Pain
Since there may be different causes of epigastric pain, it is important that you get to know, which is the reason you’re having this kind of pain. Seeing a doctor will help determine the cause.
- Physical exam: A doctor may feel the abdomen to find out if it is rigid or tender. The doctor may change or even stop medications you may be using so that the pain subsides.
- Urine or blood tests: These tests can show if you have inflammation or infection that brings the pain. The tests can help find out if the liver is working properly.
- X-ray: A doctor may order for X-rays to check your bladder and kidneys.
- Ultrasound: This is used to check the gallbladder to see if there are stones or it is blocked.
- Bowel movement sample: You can have a bowel movement sample to be tested for presence of blood. 2,3
Treating Epigastric Pain
The treatment is aimed at resolving the problem, which is causing the pain. Some of the treatment options you may get are:1,2
- Lifestyle changes: If you have epigastric pain due to overeating, taking alcohol, or food triggers, you may want to stop those behaviors.
- Anti-inflammatory medications: You may be given anti-inflammatory medication to help in calming inflammation. Antacids may help in reducing stomach acid, which backs up to the esophagus.
- Antibiotics: If the epigastric pain is being caused by conditions like peptic ulcer disease, Barrett’s esophagus, or GERD, you may be administered with antibiotics and other long term treatment options to manage the conditions. Depending on the cause of the pain, these treatments can last for months or even longer.
If the pain is occurring due to taking medications like NSAIDs, the doctor may consider stopping you from taking those medications and other ways to manage the pain are examined.
You can treat epigastric pain by using natural remedies to help soothe the stomach and enhance digestion. Some of these include:
- Funnel seeds
- Cumin seeds
- Lemon juice.
Reference List
- What’s Causing My Epigastric Pain and How Can I Find Relief? http://www.healthline.com/health/epigastric-pain
- Top 10 Causes of Epigastric Pain in the Upper Abdomen. http://www.doctorshealthpress.com/general-health-articles/causes-of-epigastric-pain-in-upper-abdomen/
- Epigastric Pain. https://www.drugs.com/cg/epigastric-pain.html
- What Is Epigastric Pain? https://www.healthgrades.com/symptoms/epigastric-pain
