What is Omentum?
Omentum is a structure with two layers that contains changeable amounts of fat. It envelops and supports structures and organs in the abdomen region. The peritoneum makes up the omentum. The peritoneum is a membrane found on the apex of the connective tissues. Its main functions are to coat the abdominal opening and envelop organs found in the abdomen area2, 4.

Types
Omentum is divided into two: the lesser omentum and greater omentum.
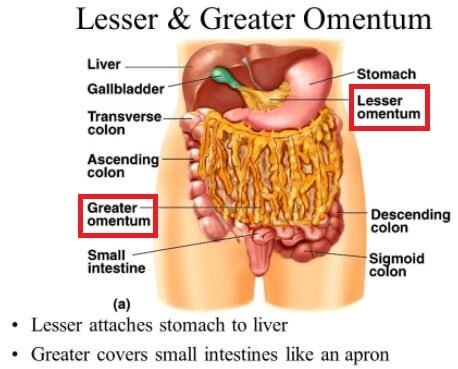
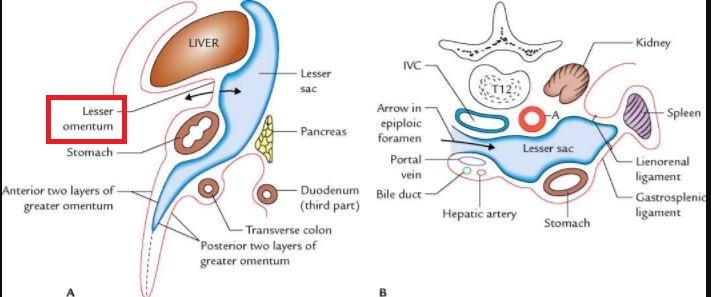
Lesser Omentum
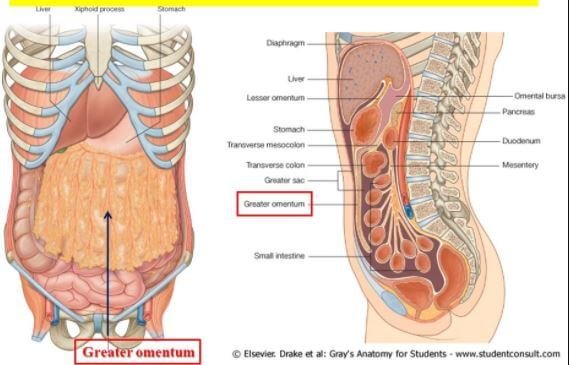
The lesser omentum is smaller than the greater omentum. It is joined to the lesser curvature of your stomach. The lesser curvature is the inside curve near the middle of your body and spans over the first section of the small intestine and the margin of the liver.
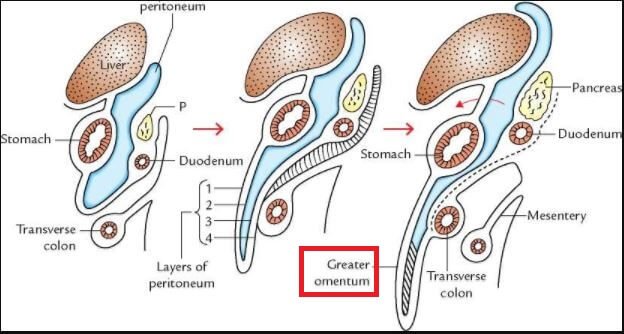
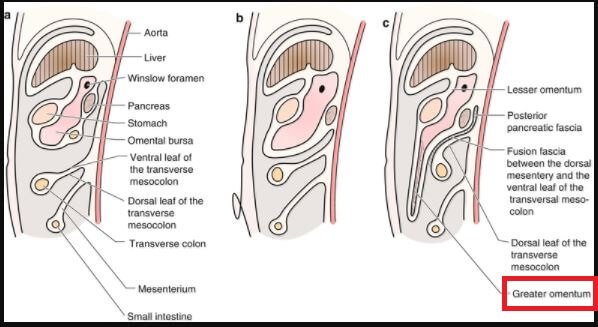
Greater Omentum
The greater omentum is connected to the greater curvature of your stomach. The greater curvature is the exterior curve located far away from the middle of your body. The omentum dangles over your colon and small intestine and it appears as an apron which collapses on itself and joins to the transverse part of the large intestine.
Functions of Omentum
Stores fat
Omentum is used to store fat in your body. Fat kept in the omentum forms a section of visceral fat while the other fat is found deep in organs.
Support the immune system
Omentum has milky spots which are clusters of macrophages. Macrophages are a form of white blood cells which help defend the body against infections. This work done by the macrophages assists your immune system which shields you against diseases.
Tissue repair and regeneration
Many researchers have shown that omentum stimulates repair of tissues. Omentum has mesenchymal stem cells which support tissue repair and regeneration. Stem cells are vital in the body because they are capable of forming other cells such as blood cells.3
Health Risks of Omentum Fat
Fats are vital in your body. Fats act as backup source of energy for the body when carbohydrates are insufficient. If the fats are excess in your body, it becomes dangerous. For instance when the omentum absorbs too much fat, it becomes harder and thicker. A swollen omentum may move the front part of your abdomen outwards thus producing a potbelly.
There are numerous healthy risk factors associated with excess fat in your body. They include:
Metabolic syndrome
These are a group of conditions such as high blood sugar, high blood pressure, too much fat around the waist, high cholesterol level among others. These conditions elevate your risk to heart diseases and stroke.
When you have any of these conditions, it does not mean you have a metabolic syndrome. But having at least one of them makes you vulnerable to serious diseases.
Metabolic syndrome is closely associated with obesity and lack of physical exercises. Having excess weight in your abdomen raises your chances of developing metabolic syndrome.5
Metabolic syndrome can cause a number of serious complications such as:
Type 2 diabetes
This is a condition that affects how your body breaks down sugar or glucose. In this condition, your body either does not make sufficient insulin to keep a normal sugar level or the body resists insulin.
Not all people can have this condition. But the following risk factors can increase your chances of getting type 2 diabetes:
Having a lot of fat in your abdomen
People who have fat stored in their abdomen are at higher risk of this illness than if fat is kept in other parts of your body such as thighs.
Being overweight
Obesity is a primary risk factor for this condition Excess weight can make your body cells more resistant to insulin which lead to high blood sugar in your body.
Lack of exercises
Leading a sedentary lifestyle without any form of physical activity leads to obesity. Without exercises your body stores a lot of sugar in the blood which causes this illness.
Illness runs in family
You are at higher risk of getting this illness if any of your family members has this disease5.
Cardiovascular diseases
These are numerous conditions that affect your heart. Examples of these diseases are atherosclerosis, stroke and heart attack.
Atherosclerosis
This is a condition where fat deposits accumulate in the blood artery wall. This accumulation constricts blood arteries making it difficult for blood to flow and reach all parts of your body. This can make you feel pain and uneasiness in your chest, a condition known as angina
Heart attack
This is a condition where a section of your blood vessel is obstructed by a blood clot. This can occur when a fat deposits in the arteries breaks away and forms a blood clot which blocks the arteries. This prevents blood rich in oxygen to flow to the heart muscles. This can damage your heart muscles and cause further complications.
Stroke
In case the artery that carries blood to your brain is blocked, it prevents blood from reaching the brain thus causing stroke.6
How to Get Rid Of Omentum Fat?
Excess abdominal fat is a cause of many serious health complications as aforementioned in this article. Reducing extra fat in your body can go a long way in promoting your overall health. There a number of lifestyle changes you can make to lower excess fat in your body such as2
Check your diet
The type of food you eat can increase fat content in your body. It is therefore important to control what you eat. You can have a diet that does not have processed foods which consist of vegetables, fruits, lean protein, low fat dairy and minimum quantities of polyunsaturated and monounsaturated fats. In case you are not sure what kind of diet to eat, you should talk to a nutritionist or dietician to help you come up with a diet plan.
Exercise regularly
Exercise is vital in weight loss and in boosting the health of your heart. You can come up with an exercise program to help you exercise. There are many exercises you can start with such as running, walking, stretching, etc. You can also talk to a physiotherapist to train you in doing certain exercises such as yoga.
Pictures
Reference List
- Omentum. https://caloriebee.com/misc/The-Omentum-and-Abdominal-Fat
- http://www.laparoscopic.md/digestion/omentum
- http://healthyliving.azcentral.com/fastest-ways-shrink-omentum-2552.html
- http://www.fearlessfatloss.com/physical-fitness/what-is-an-omentum-and-what-does-it-look-like/
- Metabolic syndrome. http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/metabolic-syndrome/symptoms-causes/dxc-20197520
- Cardiovascular diseases. https://www.bhf.org.uk/heart-health/conditions/cardiovascular-disease
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Omentum
- https://www.britannica.com/science/omentum
- https://radiopaedia.org/articles/omentum
- emedicine.medscape.com/article/191817-overview
