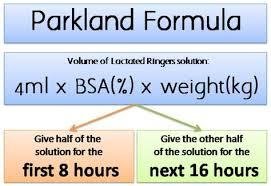
Parkland Formula Definition
Parkland formula is a formula that is used to determine the amount of fluid needed to be replaced in burn patients in a day so as to ensure that they are stable. The quantity of fluid needed in the first day usually covers the surface area of the patient’s body affected by the burn. The initial fluid is given within 8 hours after the patient has had a burn while the next one administered within 16 hours after the first one2.
Burn
Burn is an injury to your skin or tissues. A burn can be in the form of heat or thermal, chemical and electrical. The injury also causes inflammation in the area of your skin that is burnt. Your body contains substances such as histamine and serotonin which make blood capillaries more permeable as well as spread the inflammation to other parts of your body.
Medical studies have also shown that within one day after a burn, the patient’s body makes tumor necrosis factor. This substance triggers manufacture of an enzyme called nitric oxide synthetase which causes acute inflammation in body of the patient.
Besides inflammation, burns can cause shock in a patient. Burns damage blood vessels and as a result disrupt supply of oxygen around the patient’s body. This deprives body cells adequate oxygen thus causing shock and even death of body cells.
The burn also causes edema. This is a condition where excess fluids accumulate in the body tissues resulting in swelling. The patient may develop general edema if the area affected by the burn is very large.5
Classifications of Burns
Burns are classified into the following four categories according to its severity5, 6:
- Superficial thickness or first degree: This burn affects the epidermis layer of your skin. It causes pain and there are no blisters.
- Partial thickness or second degree: It affects the dermis layer of the skin. It is characterized by pain, clear fluid in the dermis and blisters.
- Deep partial thickness or third degree: The burn involves deep areas of the dermis layer of your skin. It reduces sensation and forms red staining in the affected area.
- Full thickness or fourth degree: This is a burn that affects your bones and muscles. Both the dermis and epidermis layer of your skin are damaged.
Treatment of Burns
Treatment for burns depends on its severity. Many of the people affected by the burn are treated in an outpatient facility but those who are seriously affected are hospitalized. The following groups of patients qualify to be treated in a specialized burn facility in the hospital2, 3:
- Those that the burn affects at least 10% of their dermis surface area. Patients below 10 years and those above 50 years must be taken to a specialized burn facility.
- Patients whose dermis layers burns are greater than 20% of the surface area.
- Patients who are burnt in the hands, feet, face and genital areas
- Those who are affected by electrical burns and injury from lightning
- Patients affected by chemical burns and those with inhalation injuries
Treatment for burn patient may involve the following:
- Securing the airways: Burns can cause inhalation injuries to the patients. This can affect the amount of oxygen the patient breathes and as a result deprive body cells enough oxygen.
Types of Fluid Replacement
Several fluids are used in the burn therapies such as4, 6:
Crystalloids
This is the most common used fluid in burn therapies. Crystalloid involves use of basic solution that has minerals only. It is a cheap therapy and most patients tolerate it. Crystalloids can be hypertonic or isotonic.
Hypertonic solution
This is a saline solution and various studies have recommended its use in treating burn shocks in patients. Sodium ions increase plasma osmolality and decreases cellular oedema. Hypertonic solution causes kidney failure and increases the risk of developing hypernatraemia.
Colloids
This fluid has large molecules which can prevent fluids from escaping into the bloodstream. These molecules increase the intravascular volume. Albumin and plasma are examples of colloids.
There are several plasma substitutes that can be used in burn therapy such as:
Hydroxyethyl starch
This solution is obtained from starch. It is the most commonly used plasma alternatives. This solution may interfere with blood coagulation process and in case the solution is too heavy, it may cause kidney failure and even death.
Polygelatin solutions
This solution has an average molecular weight of 35,000 and it is the cheapest plasma substitute. Polygelatin does not interfere with cross matching and coagulation problems in patients are rare as well as it does not cause kidney failure. But polygelatin has a brief lifespan in the plasma; it lasts for about four hours.
Albumin is not recommended for regular fluid replacement because its supply is limited. Another reason is that albumin is expensive than other fluid replacement products.
Ringers lactate
This is a crystalloid solution with mineral composition. Ringers lactate solution is the solution of choice in parkland formula to treat patients with burn injuries.
Parkland Formula
There are two types of parkland formula used in treating burn patients. These formulas consider factors such as burn surface area and weight of the patient prior to treatment. These formulas are1, 3:
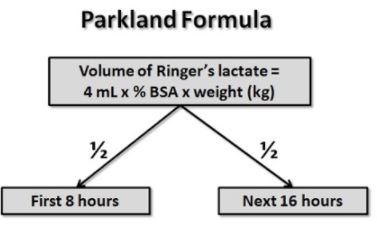
This formula is given in two phases: the first one is given for the first 24 hours when the patient was burnt. In the first day, ringers lactate solution is given to patients. The amount of the solution administered depends on whether the patient is a child or an adult. For adults, 4ml of the solution is given while 3ml for the children. In addition, ringers solution is adjusted and given to the child according to the body weight. Colloid is not used in the initial 24 hours of treatment.
In the next 24 hours, colloids is calculated according to the plasma volume and given to the patient. Glucose is added to the colloid solution to maintain the urinary output in patients. Adults and children are given different amounts of the solution. Crystalloid solution is not recommended.
Modified parkland formula

In the modified formula, ringers lactate of 4ml is given to adult patients in the first day of the burn. In the next day, colloid and albumin are used in the treatment.
Reference list
- Parkland formula. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3038406/
- Parkland formula. https://ipfs.io/ipfs/QmXoypizjW3WknFiJnKLwHCnL72vedxjQkDDP1mXWo6uco/wiki/Parkland_formula.html
- http://www.josephsunny.com/medsoft/parkland.html
- http://www.medbc.com/annals/review/vol_2/num_1/text/vol2n1p29.htm
- https://www.mdcalc.com/parkland-formula-burns
- Parkland formula. https://lifeinthefastlane.com/ccc/burns/
