What is Spleen Pain?
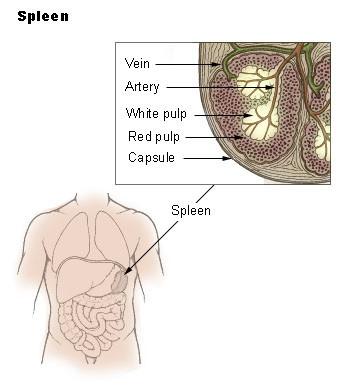
Spleen is an organ that is spongy, oval shaped and its size is that of a fist. This organ is located in the hypochondrium of the abdomen, within the area under the left ribcage.
Hypochondrim is the left upper quadrant. Spleen has many functions including helping in immune activity and storage of blood, however, it is not seen as a vital organ.
The organ can surgically be removed without causing impairment in the quality of life of an individual, however, when removed, it may cause one to be prone to infections.
Spleen pain can occur as a result of many things including conditions like rupture of the spleen and enlargement of spleen. 1
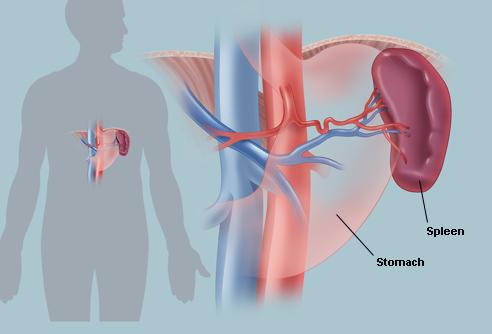
Spleen Location
Sleep Location and Anatomy
The spleen is found somewhere within the abdominal cavity. It is tucked behind the left side ribcage. If it is enlarged, it is palpable on the abdominal wall below the left costal margin. Spleen sits against the posterior abdominal wall and the diaphragm close to the ribs. It’s location close to the ribcage is quite helpful in protecting the organ, however, the same location can also be a problem to the organ. If for example, you have a fractured rib, it could piece the spleen causing it to rapture.
Further looking at the location of the spleen, it lies under the diaphragm, and in front and to the side location of ribs on the left side. Specifically, it is found on the side of the left ribs – 9th to 11th ribs and sometimes 12th rib.
Functions
- Before birth, the organ is responsible for forming blood cells, a function, which changes when a baby is born.
- After birth, the same organ that was forming blood cells takes the role of destroying those red blood cells and platelets that are worn out.
- It also helps in recycling of iron and globin component found within the hemoglobin molecule.
- Considered as the largest lymphatic organ, it assists white blood cells to spread and begin initiating the immune response when needed. The red pulp of the spleen acts as blood reservoir and helps store red blood cells, monocytes, and platelets until that time they are needed.
- The organ has the elastic splenic capsule containing smooth muscle, which contracts to squeeze blood into the circulation when required to do so by the body.
- If there are microorganisms in bloodstream, they can be trapped by lymphocytes found in white pulp after the microbes enter the spleen through the arteries.
- Lymphocytes in the spleen can also enter the circulation system to help in fighting infections in other locations.
Spleen Pain
It is difficult to identify spleen pain because the organ is close to other abdominal structures, for example – the left kidney, the stomach, abdominal wall, and the left colonic flexure. If you have pain in the left upper abdomen and the back, it could be related to the organs that surround the sleep and not necessarily the spleen itself.
Usually, spleen pain has notable features and they include a pain that aggravates when you breath or during inspiration and tends to be more prominent with deep breaths and when you sneeze. The pain may also exacerbate when you have large meals because of having a distended stomach.
Causes
Pain associated with the spleen may occur due to a number of things. The two mostly likely causes of pain of the spleen is a ruptured or infarct of the spleen. If you have a ruptured or an infarct of the spleen, you need emergency medical attention because they could be fatal if they are left unchecked.
Enlarged spleen
Although this condition is assumed to be the commonest caused of spleen pain, this is not always the case and many a time, it rarely causes pain. Splenomegaly will cause mild tenderness and discomfort.
Pain may however occur when the splenomegaly is massive. Spleen pain associated with splenomegaly may occur if there is an infection or inflammatory condition. Usually, pro inflammatory cytokines can cause painful splenitis.
When a patient has splenomegaly or enlarged spleen, there will be a dull rubbing sensation or dragging effect, particularly after taking a meal when the stomach becomes distended. In this case, a patient has a feeling of pressure and not actually a normal pain.
Mild and moderate cases of splenomegaly shouldn’t bring about notable pain of spleen. Remember that the spleen has elastic capsule muscle that can expand many times the size of the spleen and not even cause rupture.
Splenic infarct
When there is death of splenic tissue, it may be referred to as splenic infarct and it arises due to blockage of the splenic artery and its branches. An obstruction of this artery and its branches can result in prevention of oxygen-rich blood from reaching parts of the spleen.
When this occurs, it results in tissue injury because of lack of oxygen, a situation referred to as hypoxia. This, in turn, leads to an infarct. An embolus is thought to be the commonest cause of arterial blockage that results in splenic infarct.
Sleep rupture
If there is trauma directed to the upper abdominal area, it could result in rupturing of the spleen. For example, if there is a sharp force, it can make the spleen rapture.
The force causes penetration and gross hemorrhaging. Also, a blunt force trauma that causes fracturing of the rib may mean that the fractured rib penetrates the spleen causing it to rupture. In most cases, little or no blunt trauma will not cause rupture.
Spleen pain may also be caused by other things such as :
- Spenic fistulas
- Splenic abscess
Diagnosis
A doctor will conduct a number of diagnosis procedures to confirm if it is actually a pain related to spleen or it is pain arising from other organs surrounding the spleen. Depending on the cause, the diagnostic tests may include:
Physical exam
A doctor will do palpating and pressing on the abdomen area. This is specially targeted on the under area of the left ribcage. A doctor performing physical examination is able to feel an enlargement of the spleen and identify other signs that may indicate illnesses causing splenomegaly.
Ultrasound
A doctor may order ultrasound test. In this procedure, images of the abdomen area are taken through bouncing harmless sound waves just off the organ to see images of the spleen.
Computerized tomography (CT scan)
In this type of test, X-rays are used to create detailed images for the area of the abdomen. Usually, a contrast dye may be used to ensure the images are more visible.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Using magnetic waves, it helps create detailed images of a patient’s abdomen. Again, a contrast dye may be applied to help measure flow of blood to the spleen during an MRI.
Bone marrow biopsy
If it is suspected that the spleen is enlarged, a bone marrow biopsy may be ordered by a doctor. This involves a needle being inserted in a bone and taking sample of the marrow to be tested. Leukemia and lymphoma may also be diagnosed in this manner.
Liver and spleen scan
Using a radioactive dye in small amounts, it is injected into the arm and it collects in these organs. This kind of scan can also reveal if there are problems with the spleen.
Treatment
If you have spleen pain, there may be various treatment options available. The kind of treatment depends on the underlying cause and the general health of the spleen. The treatment will focus on addressing the underlying cause of the pain. Sometimes, if the spleen was injured, it may heal with rest.
A rupture of the spleen will need surgery to remove it. A doctor will conduct splenectomy where the spleen is removed using a surgical procedure.
The procedure may be done through use of small incisions through laparoscopy or it may done by using large incision through laparotomy.
When the spleen is removed, a patient will need to get vaccinations against certain types of bacteria. When a patient has a missing spleen, he or she has an increased vulnerability to getting infections.
Reference List
- Spleen Location, Anatomy and Function. Available at http://www.healthhype.com/spleen-location-anatomy-and-function.html
- Spleen Pain Location (with Pictures) and Causes. Available at http://www.healthhype.com/spleen-pain-location-with-pictures-and-causes.html
- Spleen problems and spleen pain. Available at http://www.webmd.boots.com/digestive-disorders/spleen-problems-spleen-pain
- Spleen problems and spleen removal. Available at http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/spleen-disorders-splenectomy/Pages/Introduction.aspx

There are several spelling mistakes in the article that it makes one question your credibility.
I have noticed you don’t monetize epainbody.com, don’t waste your traffic,
you can earn additional bucks every month with new monetization method.
This is the best adsense alternative for any type of website (they approve all sites),
for more details simply search in gooogle: murgrabia’s tools
Good article but proof read as spleen and sleep are close but interchanged numerous times.