What does Odor of urine tell you?
Urine usually is in straw-yellow color and under normal circumstances it has a mild, but distinct smell. The odor is not very noticeable. Certain conditions and physiological states can make urine to change its smell. In some cases, the smell of urine might signify that there are some health concerns, especially if its accompanied by other symptoms.

Hippocrates (460-337 B.C.) was the first scientist to use uroscopy (examination of urine) for diagnosing various diseases. The method was used in Middle Ages and Victorian era, and doctors sometimes even made prognosis based on examination of the urine. Although urine is now seen as a waste product of the body, it can still tell a lot about its functions [1].
Urine production
Urine is produced by the kidneys. Every kidney has around one million of its structural units- the nephrons. Nephron regulates the filtration of the blood and production of urine. in each nephron there is a glomerulus-a bundle of capillaries, which is surrounded by a capsule.
The pressure of the blood pushes water and other substances through the capillaries and the capsule, which has a special filtration membrane. Water and small molecules can pass the membrane, but cells and large proteins cannot- they get reintroduced in the blood stream.
This prevents the losing of important substances from blood. The filtrate then flows further in the nephron-renal tubule. It contains water, waste products and also important ions, amino acids and small proteins. In the renal tubule, the substances that the body needs get reabsorbed in the blood stream, but waste products travel further to the collecting ducts of the kidney and passes through the renal pelvis into ureter and then to the bladder. Urine contains:
- 95% water
- 9-23 g/l urea
- 1.8-8.4 g/l chloride
- 1.1-4.4 g/l sodium
- 075-2.5 g/l potassium
- 0.6-2.15 g/l creatinine
- 0.16-1.8 g/l inorganic sulfur
- Other compounds: phosphorus, citric acid, glucuronic acid, ammonia and others [2]
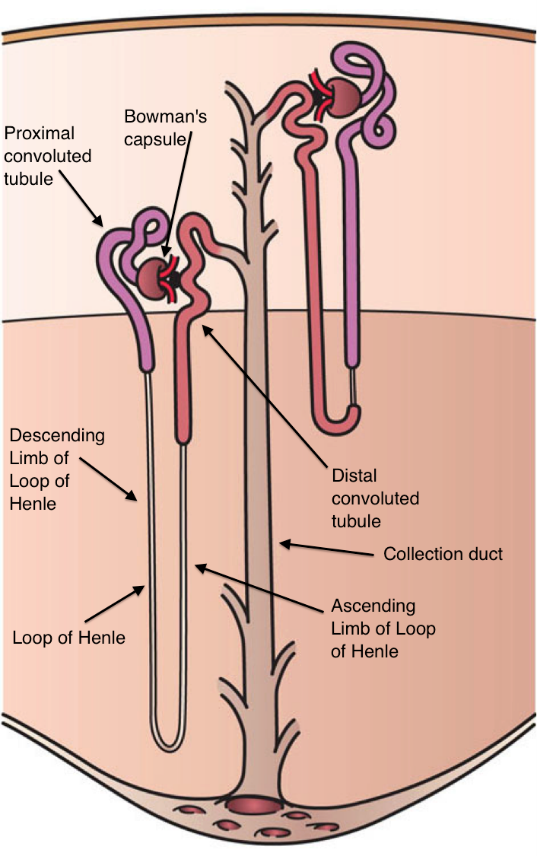
The structure of nephron
Image source: Wikipedia.org
What causes urine to change odor?
Urine usually has a distinct smell, which can change daily, depending on many factors. Diet and fluid intake has a big influence on the odor. If a person is dinking a low of water, urine might almost look like water and lack both color and odor.

But in case of dehydration, urine is usually dark and has a strong smell of ammonium. Some medications and supplements can also give urine different color and smell. There are also various conditions that can present with an unusual odor of urine, such as:
- Infection
- Gastrointestinal-bladder fistula- read about fistula forming in gallbladder in Mirizzi syndrome.
- Metabolic disorders, see 1p36 deletion syndrome
- Salpingitis- inflammation of the fallopian tubers
- Urinary tract stones
- Liver disease
- Diabetic ketoacidosis [1,4]
Sweet smelling urine causes
Sweets smelling urine can be caused by diabetes mellitus and a rare condition called maple syrup urine disease, which gives urine smell similar to maple syrup. In some cases, consuming a lot of sugar (sweets, drinks) can also cause urine to have a sweet odor, but the smell goes back to normal after excess sugar is processed [5].
Diabetes mellitus
Diabetes is a chronic condition which affects the ability to utilize the glucose found in food. There are several types of diabetes, but the three major one’s are:
- Type 1 diabetes
- Type 2 diabetes
- Gestational diabetes
In all three types of diabetes, there are disturbances in the normal function of insulin. Insulin is needed for glucose to enter cells, where it can be processed and used for energy. The cells do not take up glucose therefore the blood levels of it are high. After some time, excess glucose in the blood can damage the small blood vessels and cause serious health conditions, like stroke, blindness, kidney disease and nerve damage.
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease, where the cells of the pancreas are attacked by body’s own immune system and get damaged. In Type 1 diabetes there is very little or no insulin produced. This disease is present from an early age. Since there is no insulin produced, it has to be taken every day in order for the patient to survive. People suffering from type 1 diabetes have to measure glucose levels in their blood, plan meals and accordingly add the necessary insulin amount for the rest of their lives.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common type. It usually onsets in adulthood, but lately obesity in children and teenagers have caused the disease to affect people in younger age. In type 2 diabetes the pancreas produces insulin, but either it is produced in smaller amounts or it cannot meet the needs of the body.
It is also called non-insulin dependent diabetes, because the cells in the body become resistant to insulin. In some cases, losing weight can help the cells to become sensitive to insulin. Type 2 diabetes is usually controlled by using per oral medications at first, but later insulin injections are needed. Diabetes can also cause decreased motility of intestines, see Blind loop syndrome.
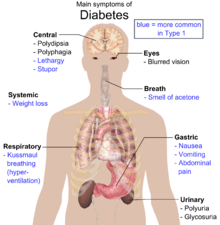
Main symptoms of diabetes.
Image source: Wikipedia.org
Gestational diabetes is a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy, usually second or third trimester. It usually resolves after giving birth, but mothers who have had gestational diabetes are at higher risk of developing Type 2 diabetes. The circulating high levels of glucose can alos be harmful for the baby [6].
Maple syrup urine disease
Maple syrup urine disease or ketoacidemia is an inherited disorder, where the body lacks certain enzymes that break down amino acids. This condition causes the urine of an infant to have a distinct, sweet, maple syrup-like odor. The infant is usually lethargic, feeds poorly, vomits and has a developmental delay.
MSUD is caused by genetic mutations in 3 genes that provide instructions for making protein complex, which is essential for breaking down amino acids- leucine, isoleucine and valine. These amino acids are present in protein-rich foods.
Since these amino acids are not processed, they build up in the body and can cause toxic effect to brain and other organs. If the disease is left untreated, it can cause seizures and death [7].

A child with maple syrup urine disease.
Image source: slideshare.net
References
- General information: http://www.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/urine-odor/basics/definition/sym-20050704
- History: http://www.doctorsreview.com/history/sep05_history/
- Urine production: http://learn.visiblebody.com/urinary/urine-creation
- Causes: http://www.nhs.uk/conditions/smelly-urine/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- Sweet smelling urine causes: http://www.livescience.com/15576-urine-colors-smells-health.html
- Diabetes: http://www.webmd.com/diabetes/guide/types-of-diabetes-mellitus#1
- Maple syrup urine disease: https://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/condition/maple-syrup-urine-disease#diagnosis

Hi blogger, i must say you have high quality content here.
Your page should go viral. You need initial traffic only.
How to get it? Search for: Mertiso’s tips go viral