What is Wrist Pain?
Wrist pain is any discomfort or pain in the wrist and carpal tunnel syndrome is a frequent cause of wrist pain. Wrist pain is quite common and can normally be successfully diagnosed and treated. [1,5,6,10]
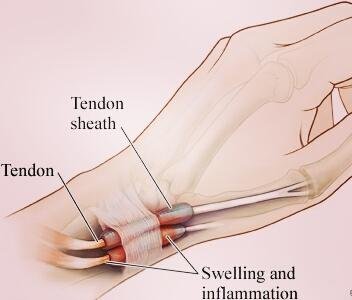
The wrist joint has a greater role in basic motions including texting, writing, and other daily chores. When the wrist is affected it can influence or interfere with your daily engagements and can be very frustrating. Everyday use of the arm, sports injuries, and work injuries are among the common causes of wrist pain.
Causes
- When any part of your wrist is damaged it can cause pain and influence your ability to use your hand and wrist. It’s very frustrating and the usual causes of this pain include the following:
- Injuries, Sprains, broken bones, and tendonitis can cause wrist pain.
- Osteoarthritis a degenerative joint disorder caused by a breakdown of the cartilage that covers the joint resulting in swelling and pain.
- Rheumatoid arthritis is a disease of the immune system which develops when the immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of your joints.
- This can cause painful swelling which may eventually result in bone erosion.
- Carpal tunnel syndrome is a common cause of wrist pain that occurs when the median nerve, which is one of the 3 major nerves in the forearm, becomes pinched or compressed from doing repetitive tasks with your hands, being pregnant, overweight or underactive thyroid.
- Ganglion cysts is a noncancerous swelling that most commonly occurs near the tendons or joints of the hands or wrist. They are round fluid-filled jellylike lumps and can be painful when they press on a nearby nerve.
- Kienbock’s disease is an uncommon debilitating condition that occurs when the lunate bone collapse due to insufficient blood supply. It can cause chronic pain and dysfunction. This occurs more in men than women.
- Gout is another cause of wrist pain which occurs when your body generates excess uric acid which forms crystals in the joint rather than being excreted in the urine.
- This can cause an agonizing pain and swelling. Drinking too much alcohol, other medical conditions including kidney disorder, and high blood pressure causes gout.
Symptoms
These symptoms could be mild or severe and some signs such as high fever, red and warm wrist could signal infectious arthritis, which is a serious illness. Other symptoms that are associated with wrist pain include:
- Redness or swelling around the wrist
- Numbness, or tingling feelings in the hands
- Swollen fingers
- Struggling when clenching a fist or gripping objects
- Warmth in a joint near the wrist
- Sudden, acute pain in the hand
- Bruising
Diagnosis
During diagnosis, your doctor will conduct a physical examination and arrange some test to diagnose the cause of your wrist pain. Depending on your symptoms your doctor will do the following:
- The physical examination your doctor will do involves bending your wrist forward and tapping the median nerve part to see if you feel numb, pain or tingling. Your doctor may also ask you to carry some objects to test your grip.
- An X-ray of your wrist may be done to assess the joints and bones.
- Your doctor may also order an electromyography to evaluate the health of your nerves.
- A blood and urine test can be conducted to identify any crucial medical conditions.
- A nerve conduction velocity may be carried out to test for nerve damage.
- A small sample of fluid from your joints may be removed to test for calcium, crystals, or if you have gout, an infection or pseudogout.
Treatment
Treatment of wrist pain varies greatly, based on how severe it is, the location, age, your overall health, and type. Here are some common treatments of wrist pain:
- Painkillers such as paracetamol, naproxen or ibuprofen are recommended to help relieve inflammation, pain and to avert joint damage.
- Your doctor can recommend Cortisone injections to help with the symptoms.
- For severe cases of carpal tunnel syndrome, a surgery is recommended to repair the median nerve.
- A physiotherapist could recommend specific treatments and exercises to help reduce wrist pain and aid in the healing process.
- A surgery may be done to if necessary to repair ruptured ligaments or tendons.
- Ensure your wrist gets adequate rest and use a pillow to help elevate your wrist.
- Ice would be helpful for acute injuries in reducing swelling and controlling pain.
- Heat application is also beneficial for chronic injuries. It helps ease off and loosen tissues and enhance blood flow to the area. Ensure to use a moderate heat for a short time to avoid burns.
Prevention
- Always keep your wrist straight instead of bending them when using a keyboard or mouse, driving, riding a bike, chopping, knitting, and using different tools.
- When doing activities that need repetitive wrist and finger movements ensure to take breaks more frequently.
- Prior to starting an activity, moderately warm up your fingers and wrists.
- Wear properly fitting shoes to prevent falls because falling forward onto an overstretched hand causes wrist injuries.
- In the case that you are involved in high-risk activities such as snowboarding, rollerblading or football, make sure to wear wrist guards.
Homecare
Home care remedies can help reduce inflammation and pain and also avert further damage. Here are some home care tips you can consider:
- For a minor injury, you could try applying ice on it or massage ice on the affected area to help reduce the pain and swelling.
- Wrap your wrist with an elastic bandage and rest it as much as possible.
- Take painkillers such as paracetamol for pain relief.
- Refrain from activities that aggravate your pain.
- When going to sleep wear a wrist splint to help reduce swelling. In the case of a recent injury, wear the wrist splint for few days.
- You can also learn from a physiotherapist the best wrist strengthening and flexibility exercises you can undertake.
- Do not overdo the exercises, if you feel pain stop the exercise and ensure your wrist gets adequate rest.
Reference List
- www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/wrist-pain/basics/definition/con-20031860
- www.medicinenet.com/wrist_pain/symptoms.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003175.htm
- www.physioworks.com.au/Injuries-Conditions/Regions/wrist-pain-injury
- https://en.m.wikipedia.org/wiki/Wrist_pain
- Wrist pain. Available at www.physio.ie/injuries-conditions/wrist-pain/
- www.nytimes.com/health/guides/symptoms/wrist-pain/overview.html
- Wrist pain. Available at https://www.dignityhealth.org/Service|%20Areas/bayarea/services/orthopedics/orthopedic-conditions/wrist-conditions-injuries/wrist-pain
- www.mayoclinic.org/disease-conditions/wrist-pain/basics/causes/con-20031860
- www.healthline.com/symptoms/wrist-pain
- Wrist pain. Available at www.webmd.com/pain-management/carpal-tunnel/carpal-syndrome-home-treatment
