What is greasy stool?
Greasy stool is usually described as yellow, voluminous diarrhea, that has an unpleasant smell. Sometimes it is hard to flush the stool down the toilet, since it is too oily. It can also float on the water, or patients might notice oil droplets in the water. Greasy stool is also known as steatorrhea- Latin word for excess fat in stool. More commonly occult steatorrhea is present- a condition where excess fat in the stool is not so easily noticeable, but stool has high amounts of fat in it [1,2].

Greasy diarrhea can be a symptom of many conditions.
Image source: steatorrhea.org
Causes
Diet factors
There are various diet factors that can cause greasy stool. Usually this is a transient occurrence and once the diet is changed, the stool normalizes. Foods that can cause greasy stool are:
- Nuts
- Fatty fish
- Jojoba oil
- Olestra-used for packaged foods to minimize fat and calorie count while keeping their texture. The body cannot digest it and it is excreted in the stool. If this dietary factor is not recognized, it can lead to the diagnosis of malabsorbtion
- Potato chips[2]
Pancreatic conditions
Pancreas has many functions that are very important in the digestive process. One of the enzymes that the pancreas produces is lipase. Lipase, together with bile helps to break down and digest lipids from the food. In case there is shortage of this enzyme, lipids are not properly digested and that causes the excessive amount of fat in the stool. In case the pancreas is damaged in some way, it might cause shortage not only of lipase, but of other enzymes too. These conditions include:
- Acute and/or chronic pancreatitis
- Pancreatic tumors
- Trauma
- Pancreatic surgery
- Cystic fibrosis in pancreas
- Other diseases of pancreas, including genetic disorders, like Li-Fraumeni syndrome[3]
Gallbladder and biliary tract conditions
Gallbladder is an organ that stores bile- a chemically active fluid produced by the liver. Bile is essential for proper lipid digestion. Its main function is to dissolute fat droplets, so that the pancreatic enzymes can continue the digestive process. In most cases, problems are seen in people after gallbladder removal surgery, who continue to eat large amounts of fatty food. The bile is still produced, only it is drained in the small intestine and is not able to work on large amounts of fat. Greasy stool can also be present in patient with the following biliary system disorders:
- Gallstones, if they obstruct the bile duct
- Gallbladder cancer
- Bile duct cancer
- Primary biliary cirrhosis
- Primary sclerosing cholangitis [1]
Small intestine conditions
In case the mucosa of small intestine is compromised, lipids can’t be absorbed. This can cause greasy stool. Conditions that can cause this are:
- Celiac disease
- Crohn’s disease
- Surgical procedures
- Whipple’s disease [1,2]
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome- a condition that causes tumor growth in pancreas and small intestines. In this syndrome there are elevated levels of gastrin, which causes excess acid production in the stomach, which leads to various other problems, including fat malabsorption [4].
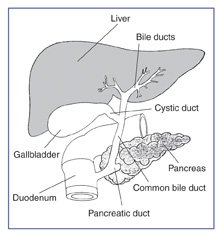
Anatomy of duodenal, liver and pancreatic region. The bile ducts and pancreatic ducts open in the duodenum through one common opening.
Medications
There are some medications that can cause excess fat levels in the stool. These include:
- Weight loss pills
- Statins- medication used for lowering cholesterol levels in the blood
- Octreotide and Lanreotide- drugs used for acromegaly [4,5]
Diagnosis
If the patient complains about greasy stool, the underlying cause for it should be found.
Blood analysis
-
- Liver enzymes
- Pancreas enzymes in blood, such as lipase
- Inflammation markers
- Gastrin levels-to exclude Zollinger-Ellison disease [5,6]
Imaging studies
- X-ray can be used to diagnose calcifications in pancreas
- Ultrasound imaging can show inflammation of the gallbladder, gallstone and signs of pancreatitis
- Endoscopic retrograde cholecystopancreatography- a diagnostic test, which allows to visualize structures in bile system and pancreas. A scope is inserted through mouth till duodenum, and through papilla Vateri- the opening of pancreatic and bile ducts in duodenum, a dye is injected to visualize pancreatic and bile ducts
- CT and MR imaging can show various pathological changes in liver, pancreas and small intestine [5]
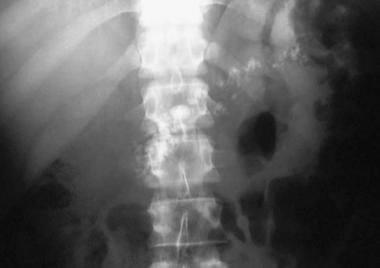
X-ray image of abdomen in patient with chronic pancreatitis. Calcifications can be seen where the pancreas is located.
Image source: emedicine.medscape.com
Other tests
Other tests might include:
Function tests of intestine absorption:
- D-xylose absorption for proximal small intestine function
- Schilling tests and bile breath tests for distal part of small intestine
- Tests for bacterial overgrowth syndrome
Barium contrast tests and biopsy should be performed, if there are any structural abnormalities. Gastroscopy is usually also performed to detect structural abnormalities [5].
Treatment
Greasy stool is usually only a symptom of underlying condition.
- Diet should be checked for any products that might cause steatorrhea, and these factors should be prevented
- Pancreatitis- in case of chronic pancreatitis, treatment approach should be to intake extra enzymes to help digestion. 30000 units of lipase should be used with every meal
- If enzyme therapy is unsuccessful, enzymes should be protected from gastric acid. H2 blockers can lower the hydrogen ions and protect enzymes.
- Use of proper diet is crucial for patients with celiac disease [6].
Complications
If steatorrhea is left untreated it can cause several health problems. Main cause for it is lack of fat-soluble vitamins- K, A, D, E [1].
If you found this article helpful, share it on social media. For your comments and personal experience use the comments section below.
References
- General information: http://www.health-tutor.com/greasy-stool.html
- Causes and treatment: http://www.steadyhealth.com/medical-answers/causes-and-treatment-of-steatorrhea-oily-stool
- Pancreas diseases: https://www.pancan.org/facing-pancreatic-cancer/diet-and-nutrition/pancreatic-enzymes/
- Zollinger-Ellison syndrome: http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/zollinger-ellison-syndrome/basics/definition/con-20024097
- Diagnostics: http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/180785-workup#c3
- Treatment: http://www.diagnose-me.com/symptoms-of/steatorrhea.php

Hi. I see that you don’t update your blog too often. I know that writing articles is boring and time consuming.
But did you know that there is a tool that allows
you to create new posts using existing content (from article directories or other websites from your niche)?
And it does it very well. The new articles are high quality and pass the
copyscape test. You should try miftolo’s tools