What is Leukopenia?
Leukopenia refers to the drop in the count of white blood cells in an individual’s body. Leukopenia is also known as Leukocytopenia. White blood cells are part of the immune system and protect you against infections4.
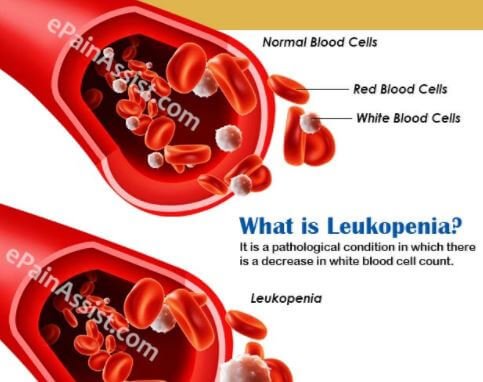
When you have an infection or inflammation, the counts of white blood cells increase to fight the infection in the body. But in some cases, the number of white blood cells decreases due to other medical conditions such as autoimmune disorders and medications. This weakens your immune system and reduces its ability to fight infections.
Types
Leukopenia can be classified into the following1, 6:
Neutropenia
This is the most common type of leukopenia. It refers to a drop in the number of circulating neutrophil which is a form of granulocytes. Neutrophil constitute a large count of white blood cells. Other types of granulocytes include basophils and eosinophils. Neutrophil help fight bacterial, viral, fungal and parasitic infections in the body. Therefore a decrease in the count of neutrophil makes you more vulnerable to the aforementioned infections.
Lymphocytopenia
This is a form of leukopenia where there is a low count of lymphocytes in your body. Lymphocytes are responsible for defending your body against viral infections. Fewer lymphocytes in the body will increase your chances of being infected with viral diseases.
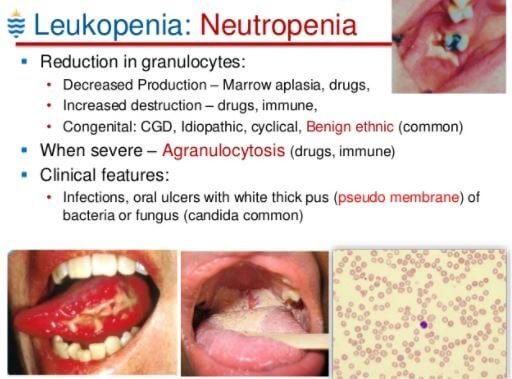
Causes
Leukopenia can result from numerous causes such as2, 3, 5, 6:
Medications
There are certain types of medicines that can decrease the count of white blood cells in your body. They include interferons, bupropion, sodium valproate, steroids, penicillin, etc.
Autoimmune disorders
Autoimmune disorders that cause leukopenia occur when your immune system wrongly attacks and destroys white blood cells and bone marrow tissues in the body. Examples of autoimmune disorders are lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Malnutrition
Insufficient minerals and nutrients in the body can cause leukopenia. Your body needs certain minerals and nutrients to perform it functions well. These minerals and nutrients include zinc, copper, Vitamin B12 and folate. Deficiency in the above minerals and nutrients impairs bodily functions including manufacture of white blood cells.
Bone marrow disorders
There are conditions that affect your bone marrow impairing its functions of producing white blood cells. These conditions include:
- Aplastic anemia– This is condition that cause bone marrow to stop manufacturing new blood cells. Normally stem cells in the bone marrow make red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. Damage to stem cells impairs its functions as result leading to low count of white of blood cells.
- Myelodysplastic syndrome: These are a group of blood disorders that lower the number of blood cells in the body. Myelodysplastic syndrome occurs when the stem cells in the bone marrow are defective thus unable to perform their function.
Cancer
Different forms of cancer can cause leukopenia. For instance leukemia can cause leukopenia.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy
These methods are used to treat cancer. Chemotherapy uses certain drugs to destroy cancerous cells. Radiation therapy uses radiation to kill malignant cells. These treatment methods can damage your bone marrow which impairs its function of making new blood cells.
Congenital disorders
These are disorders that occur at birth. Congenital conditions can affect how your bone marrow manufactures new blood cells. Examples of congenital disorders that cause leucopenia include myelokathexis and Kostmann syndrome.
Other causes of leucopenia include:
- Viral infections that affect bone marrow can lead to a drop in the number of white blood cells in the body.
- HIV/AIDS and tuberculosis can also cause leucopenia
Symptoms
Leucopenia does not usually cause symptoms. But the following are common symptoms of this condition1:
- You may have headache and fever. You may also feel general fatigue in your body. You may be prone to infections. You may also have to urge to sleep anytime.
Diagnosis
- Leucopenia can be diagnosed through a complete blood count. This test is done to measure the amount of blood cells in your body and it is effective in checking for medical disorders that affect your health. This test measures red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets2, 6.
- Before the test, you should eat normally unless your doctor tells you not to eat for some time prior to the test. This is useful when additional tests need to be done on your blood sample.
- During this test, your doctor collects a sample of blood from your vein especially on your upper arm. The test is easy and takes less than five minutes. The sample is the analyzed in the laboratory. The results will be out after several hours or a day.
- In case the results show unusual levels of blood cells, your doctor may order other tests to identify the cause.
Treatment
Treatment for leucopenia is based on the form of white blood cells that is low and underlying condition causing it. The following are some of the treatment options5, 6:
Medications
Drugs can be used to trigger your body to produce more blood cells. Your doctor can prescribe certain medication to increase low count of blood cells. Antifungal or antibiotic drugs can be recommended to treat fungal and bacterial infections respectively.
Radiotherapy/Chemotherapy
In some cases, your doctor may advise you to discontinue certain treatment to allow your body to make new blood cells. Your blood cells increases during radiation or chemotherapy sessions. Therefore stopping these treatment methods can help your body replenish white blood cells.
Growth factors
If leucopenia is caused by genetic factors or chemotherapy, growth factors obtained from bone marrow can help. These growth factors encourage your body to make more white blood cells.
Diet
A healthy diet can be recommended to increase the count of white blood cells in your body. A low-bacterial diet is good because it lowers your chances of obtaining germs from food.
There are some self-care measures you can take to prevent infections when your white blood cells are low. They include:
- Eat healthy food– Your body requires nutrients and nutrients to heal from illness. Eat a lot of fruits and vegetables.
- Have enough rest– You need to plan your activities so that there is time to rest. Resting will help you heal.
- Wash your hand properly– Wash your hands well using soap to get rid of germs. Germs can cause infection if they enter your body.
Reference List
- http://illinoiscancercare.com/blood-disorders/blood-disorder-types/leucopenia/
- https://www.news-medical.net/health/What-is-Leukopenia.aspx
- http://www.medindia.net/patients/patientinfo/leucopenia.htm
- http://leucopenia.org/en/complications/
- https://herbpathy.com/Herbal-Treatment-for-Leucopenia-Cid4997
- https://www.healthline.com/health/leukopenia#risk-factors4

2 comments