What is Shoulder Pain?
Shoulder being a ball and socket joint, it has 3 main bones known as the humerus (long arm bone), the clavicle (collarbone), and the scapula also called the shoulder blade which is covered by a cartilage.
The shoulder joint is made up of two main joints, the acromioclavicular and glenohumeral joints which allow the shoulder to move back and forth, the arm to move in circular motions, upward and away from the body. [6, 7]
Shoulder pain is when you feel a great deal of discomfort and pain when you try to move your shoulder. The rotator cuff brings about the movement in the shoulder and when it’s torn you’ll have difficulties or pain when moving your arm. Shoulder pain is a common problem, and majority of people experience it at night.
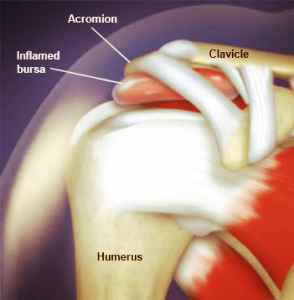
Causes
The shoulder is a ball and socket joint and it is gullible to injury. Shoulder pain can be caused by a number of factors including:
- Shoulder joint instability
- Pinched nerves
- Dislocation
- Labral tear
- Shoulder arthritis
- Strains from overexertion
- Frozen shoulder
- Tendonitis from overuse
- Broken fracture
- Some other uncommon causes of shoulder pain are an infection, nerve-related problems, and tumors.
Symptoms
Shoulder pain is in itself a symptom and can be a long-term problem if not diagnosed and treated in time. One can use painkillers like ibuprofen or ice packs to relieve pain and decrease inflammation. Here are some symptoms of shoulder pain and they require immediate health care:
- Sudden swelling
- Exposed bone or tendon
- An inability to raise your arm
- Severe pain
- Deformity to the shoulder
- Signs of an infection
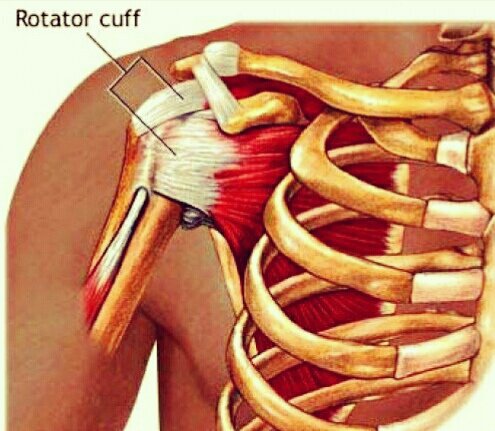
Diagnosis
During diagnosis, your doctor will want to figure out what causes your shoulder pain. He or she will inquire from you about the pain you feel and perhaps conduct a physical examination. The doctor will feel for the differences between the shoulders, swelling, tenderness, redness, and signs of dislocation. The shoulder joint may be moved to see if any distinct motion causes pain.
Further tests may be needed based on the first diagnosis, including:
X-rays
Plain X-rays can show detailed images of your shoulder joint to assist in the diagnosis.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
This imaging procedure can show better and detailed images of your shoulder joint. It will enable your doctor to detect injuries to the tendons and ligaments around your shoulder joint.
Arthrogram
This test uses X-ray to get a series of images after a dye has been injected into the shoulder.This test enables your doctor to see the ligaments, tendons, cartilage, your joint capsule, and muscle so he or she is able to identify where the problem is.
Computed tomography (CT) scan
Using specially designed X-ray cameras CT scan produces cross-sectional images of the shoulder. This helps the doctor see the soft tissues and bones in your shoulder to identify abnormalities.
Arthroscopy
This is the kind of keyhole surgery using a fiber-optic camera to see inside your shoulder joint and correct any damage.
Treatment
The treatment of shoulder pain is always based on the symptoms and the cause of the pain. It’s crucial that you consult your doctor before starting a treatment program so that you’ll be able to know how serious your condition is and what treatment program to embark on.
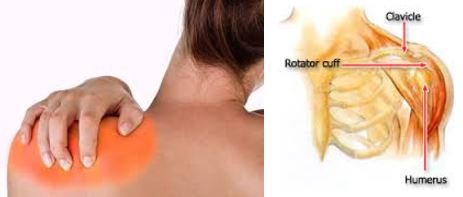
Here are the treatment options a doctor may use to help your situation:
Changes in activity
This involves resting your shoulder, changing your activities and physical therapy to allow your shoulder to improve its flexibility and strength. Also, take caution because extended immobilization can bring about frozen shoulder.
Icing
Using ice packs for minor injuries is a common treatment method for shoulder pain. To help reduce the pain one should ice their shoulder 15 to 20 minutes four times or thrice a day for several days. Wrap ice in a towel or use an ice bag to avoid having burn skin or frostbite.
Medications
The generally known medication prescribed for shoulder pain is Nonsteroidial anti-inflammatory pain drug also called NSAIDs especially if the cause of shoulder pain is bursitis, tendonitis, and arthritis. This drug can also be injected into your shoulder as recommended by your doctor.
Surgery
About 90% of patients with shoulder pain react positively to simple treatment methods but there are cases that would require surgery such as some rotator cuff tears and recurring dislocations. Arthroscopy can be done to repair tone tissues or to get rid of scar tissue, or an open procedure for shoulder replacement or larger reconstruction.
Complications
Stiffness
This can happen to about 10% of people after surgery. It’s common in senior adults and after rotator cuff repairs. Physiotherapy can help improve it or a steroid injection or hydrodilatation and the stiffness may disappear in a year.
Pain
With every surgery comes pain and your doctor will give you medications to control the pain and it’s crucial you take it as instructed.
Rotator cuff damage
The muscles of this part of the shoulder are susceptible to injury after surgery and a surgeon would always have to make all efforts to reduce damage to the soft tissue. As for the patients, he or she has to learn which movements are risky to the healing shoulder and which are safe.
Homecare
Some of the shoulder pain can heal gradually at home if well taken care of and done as recommended by your doctor. Here are some homecare tips to follow to help in the healing process:
- To help decrease pain and inflammation one can use ibuprofen or acetaminophen.
- A physical therapist can recommend to you some exercises to do at home which can help strengthen your shoulder muscles and rotator cuff tendons.
- To keep your tendons and shoulder muscles in their correct posture, practice good posture daily.
- Use ice on the painful shoulder. Wrap the ice in a towelor use an ice bag to avoid having frostbite, put the ice on for 15 to 20 minutes thrice or four times daily for 2 to 3 days.
Reference List
- https://www.verywell.com/shoulder-pain-2548793
- http://www.webmd.boots.com/pain-management/guide/shoulder-pain
- Shoulder pain – https://familydoctor.org/shoulder-pain/
- Shoulder pain. Available at www.nhs.uk/conditions/shoulderpain/Pages/Introduction.aspx
- www.orthoinfo.aaos.org/topic.cfm?topic=A00065
- Shoulder pain. Available atwww.mayoclinic.org/symptoms/shoulder-pain/basics/definition/sym-20050696
- Shoulder pain – Causes & Treatment at www.healthline.com/symptoms/shoulder-pain
- www.medicinenet.com/shoulder_pain/symptoms.htm
- https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/003171.htm
- Shoulder pain. Available at https://www.shoulderdoc.co.uk/article/1473
- https://www.arthritis-health.com/surgery/shoulder-surgery/total-shoulder-replacement-risks-and-complications
