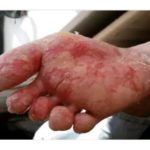
What Is Gram Positive Cocci In Clusters?
Gram Positive Cocci In Clusters Is easy for medical lab technologist to identify the appearance and arrangement of Gram positive cocci. A report showing Gram positive cocci appearing in clusters has an indication that after a culture test, staphylococcus species of bacteria will be identified.
This is an initial evaluation that shows the likelihood of a true pathogen staphylococcus aureus will be present or there is will be skin contaminant indicated by the coagulase negative staphylococci (CNS).
Types of Bacteria
There are three fundamental types of bacteria;
- Bacillus- are rod shaped
- Coccus- are spherical shaped
- Spirillum- are spiral shaped
Coccus originate from the micrococcaceae family and are sperical in shape. They usually have a diameter that is less than 1µ. Pathogenic coccus are further divided into staphylococcus (clustered) and streptococcus (short or long chains) as shown below.
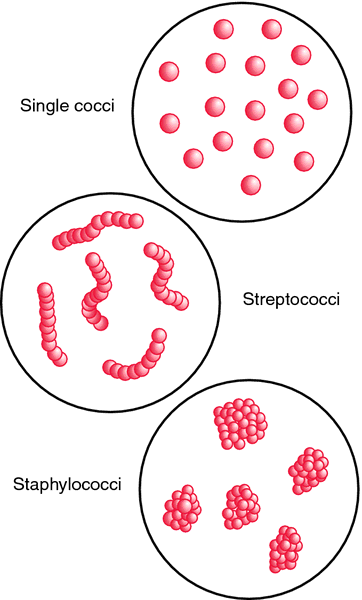
Staphylococci and streptococci are both gram positive and do not develop spores. Staphylococci cause severe infections such as furuncle and carbuncles while streptococci are responsible for sore throat and septicemia.
What does Gram Positive mean?
In the Gram staining test, the characteristic of bacteria is determined as whether it is positive or negative. Gram positive bacteria always retain the crystal violet stain color. Bacteria that read positive often possess a cell wall, which has a thick layer of a substance known as peptidologlycan.
Staphylococci
For staphylococci, staphylococcus aureus is usually the commonest pathogen as it causes pneumonia, osteomyelitis, skin infections, and endocarditis.
Some strains have toxins, which cause more severe conditions such as scalded skin syndrome, gastroenteritis and staphylococcal shock syndrome. The types of infections include:
1. Staphylococcal osteomyletis
This is prevalent in children and is associated with fever, chills as well as pain around the involved bone.
Staphylococcal shock syndrome
This mainly caused by skin infection, burn infection, wound infection (after operation) and vaginal tampon use. Commonly resulted by methicillin-susceptible staphylococcus aureus and methicillin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (is on the rise).
Staphylococcal pneumonia
This could either be the primary infection or have been caused by the hematogenous spread of staphylococcus aureus which results because of factors such as catheter infection. Symptoms are like lung abscess. It may develop in patients:
- Who have Influenza
- That have been diagnosed with chronic bronchopulmonary disorders
- Are using immunosuppressant
Staphylococcus endocarditis
This is a chronic febrile disease that is characterized by abscess, subconjunctival hemorrhage, heart failure that is caused by valve damage. It commonly develops in patients who have prosthetic heart valves and drug abusers. Staphylococcus aureus is the most common causative agent for this ailment.
Causes
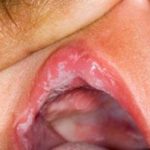
This occurs commonly in infants and under- fives. Toxins known as exfoliants which causes exfoliative dermatitis that is recognized by formation of bullae and skin peeling. Bullae are cavities which appear like bubbles and may be filled with either air or fluid.
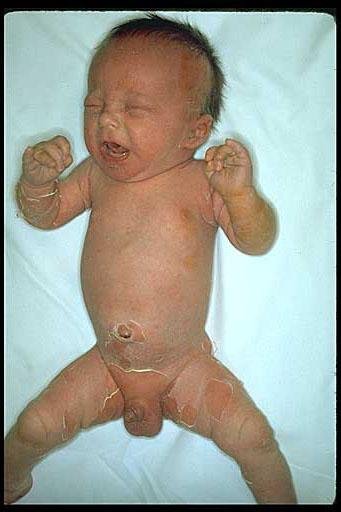
Fig.3 Infant with staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome
Food poisoning
When you take food that contains staphylococcal bacteria, food poisoning is the end result. Food becomes contaminated if the person handling has active skin infections. Cooked food is left under normal room temperature for long and if the food was not cooked properly.
Taste and color are not the best criteria to judge if food is safe or not as it may be preserved even if the food is contaminated. Symptoms of food poisoning include:
- Serious nausea and explosive vomiting which may be noticed 2-8 hours after eating the contaminated food
- Abdominal pain
- Severe diarrhea.
Neonatal infections
This occurs in neonates and symptoms may present themselves about 6 weeks after delivery. Infections include pneumonia, meningitis, skin lesions and bacteremia.
Modes of Transmission
For most diseases caused by staphylococcus, transmission is through direct tissue invasion. You may acquire diseases from:
- Patients who already have the staphylococcus infection
- Healthcare providers including physicians, doctors, and nurses
- Objects in the health facilities.
Risk Factors
Although everyone is susceptible to staphylococcal infection, some individuals are highly at risk. This group includes:
- Patients with chronic diseases such as leukemia, tumors, bronchopulmonary disorders, and influenza
- Individuals who have an implanted prosthesis, intravascular catheter or a transplant
- Neonates and lactating mothers
- Patients who are under adrenal steroids irradiation or have undergone antitumor chemotherapy.
- Drug users who use injections.
Diagnosis
To diagnose presence of staphylococcus bacteria, gram strain and culture is conducted. Different staphylococci diseases are diagnosed differently.
Scalded skin syndrome
Cultures are taken from urine, blood, umbilicus, nasopharynx or any other infection area. To confirm the presence of the bacteria biopsy of the affected area is done.
Food poisoning
If food poisoning is suspected, the medics will definitely conclude this based on the number of people showing the same symptoms. Staphylococci are usually isolated from the contaminated food. The food is tested for the presence of enterotoxins, which develop when the conditions are suitable.
Osteomyletis
Performing x-ray for the diagnosis of osteomyletis is not a good choice because it only manifests itself after about 14 days. CT scans, MRI or radionuclide bone scans are more effective and can detect earlier as compared to x-rays. To identify pathogens, bone biopsy is conducted.
In other facilities, screening is done on every patient before admission to safeguard other patients from contracting Methicilin-resistant staphylococcus aureus (MSRA). ICU patients, those with a history of MRSA or those who have undergone cardiac and orthopedic surgery are more likely to undergo screening as they are more at risk. Benefits of screening are:
- Prevent spread of MRSA
- Infections from hospitals (nosomical) will be minimized
- Isolation of carriers will enhance treatment
Antibiotic Resistance
Staphylococcus strains usually produce enzyme penicillinase which inactivates the action of several antibiotics. This is why most strains are resistant to penicillin in the forms of ampicillin, antipseudomonal penicillin and penicillin G. Vamcomycin are best used to fight MRSA.
Bloodstream infections are treated with daptomycin and vancomycin while televancin, linezolid are used for pneumonia treatment. The doctor always prescribes the dosage depending on:
- The infected area. Whether it is the skin, lungs or heart the medication will be prescribed to treat it.
- Severity of the disease. If the infection is not extensive, treatment will involve fewer medications.
- Resistant strains- if you have developed resistance to antibiotics, vancomycin or other drugs will definitely be prescribed for you.
Prevention
- A doctor should wash hands thoroughly from one examination to the next to safeguard his or her patients
- High risk patients who are carriers should be isolated and treated so as to minimize spread
- Food preparation should be done appropriately. Handling food should be done with clean hands. Food should be cooked well and if not eaten at the moment, it should be refrigerated immediately.
Treatment
When treating staphylococcus bacterial diseases are treated through:
- Intravascular catheter removal
- Administering antibiotics such as vancomycin
- Abscess drainage
- Necrotic tissue debridement.
References
- Gram Positive Cocci. Available athttp://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/Gram-positive+cocci
- Gram Staining. Available at http://www.medicinehack.com/2012/02/gram-staining-procedure-mechanism.html
- http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/gram-positive cocci/staphylococcal-infections
- Gram Positive Cocci in Clusters. Available at http://old.infectionnet.org/therapy-recommendations/vascular/empiric-therapy-of-bacteremia/gram-positive-cocci-in-clusters/
- Gram Positive Cocci. Available at http://www.merckmanuals.com/professional/infectious-diseases/gram-positive-cocci/staphylococcal-infections