What is Dry Heaving?
Dry heaving is the act of retching without passing any vomit. This may appear on its own or can be a symptom of a medical condition. It can be very uncomfortable but there are remedies that can minimize the occurrence of dry heaving [1, 2].

Although it may look similar to vomiting, dry heaving or retching is the reverse peristalsis of the stomach and esophagus but without the passage of any vomit. It may appear on its own or after vomiting when there is no more stomach content to pass. Dry heaving occurs with nausea and vomiting because they are being controlled by the same part of the brain [1, 2, 3].
When an individual dry heave, there is a spasmodic respiratory movement against a closed glottis. The antrum of the stomach contracts and the cardia and fundus relaxes. Exerting inspiratory efforts on a closed glottis causes a negative pressure in the stomach. This type of pressure will result in the herniation of the abdominal esophagus and cardia in the thoracic cavity [4]. Figure 1 shows the part of the stomach that are involved in dry heaving.
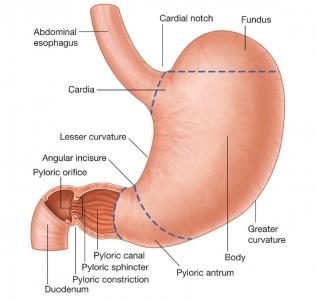
Figure 1- Parts of the stomach
Causes
Pregnancy
During the first and second trimester of pregnancy, a pregnant woman may manifest with retching or dry heaving possibly due to hormonal changes in their body. The dry heaving usually disappears during the sixth month of pregnancy [1].
Stress and anxiety
Retching is one of the most common manifestations of overwhelming stress. The appearance of this symptom does not indicate any mental health problem. It disappears once the presenting stress has been managed [1].
Food poisoning
The poisoning of food occurs when the strains of bacteria, viruses or parasites contaminate the food or drink. The most common type of food poisoning that may occur is salmonellosis which is caused by the salmonella bacteria.
Salmonella may contaminate chicken or egg that is not cooked appropriately. Research suggest that the possibility of food contamination increases if the food is not kept at 140°F and above or below 40°F. Other symptoms of food poisoning may include abdominal cramps, loose bowel movements, the presence of blood in the stool, and dehydration [1].
Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
The medical condition GERD causes stomach acid or stomach content to go back into the esophagus. This produces symptoms such as a heartburn or a burning sensation in the throat, sour taste in the mouth, difficulty in swallowing and dry heaving [1].
Pertussis
Whooping cough or pertussis is known as a very contagious infection caused by bacteria. Although infants are the most affected population, those who in other age groups may get sick with pertussis as well. Sometimes the coughing fits of those with pertussis are so severe that it causes dry heaving [1].
Chemotherapy drugs
One of the most common side effects of undergoing chemotherapy treatment is dry heaves. The chemotherapy drug acts on the medulla oblongata which is the vomiting center in the brain. It will cause a continuous contraction in the smooth muscles of the esophagus, stomach, and intestines. The result will be or dry heaving or vomiting during or after the therapy [1].
Low blood sugar
Those who are diagnosed with diabetes may present with dry heaving due to the presence of increased amounts of ketones in their system. This chemical appears as a result of the fat breakdown in the body.
Fat is metabolized into energy if there is not enough carbohydrate to convert into energy. Consuming the right amount of carbohydrates is essential in order to avoid the metabolism of fat that produces the ketone. Other symptoms that may be seen include the presence of cold, clammy skin, tachycardia or increased heart rate and nausea [1].
Remedies
The frequency or severity of dry heaving can be minimized by observing the following measures [1, 3]:
- Relax or engaging in recreational activities to reduce the anxiety or stress that is present.
- If the feeling of dry heaving appears, avoid lying down and sit down in a well-ventilated room to reduce the discomfort.
- Individuals with GERD should avoid carbonated drinks because it may aggravate the symptoms.
- Pregnant individuals who find dry heaving to be bothersome should consult their physician before taking any medication.
- Those with diabetics should ensure that they have normal blood sugar. They should consume food that would increase their blood sugar immediately
- Preparing the food correctly will prevent the occurrence of food poisoning. Uneaten food should be stored in the refrigerator to last longer. Food with a suspicious smell should be thrown away and not consumed.
If the symptoms of dry heaving appear more frequently, a physician should be consulted to possibly receive medications to reduce the discomfort caused by dry heaving [1, 2, 3].
References
- Wu, K. (2016, February 21). How to Stop Dry Heaving: Causes and Treatment. Retrieved from Wow Remedies: http://www.wowremedies.com/how-to-stop-dry-heaving/
- Cunha, J. P. (2016, March 2). Vomiting and Nausea. Retrieved from eMedicine Health: http://www.emedicinehealth.com/vomiting_and_nausea/article_em.htm
- Healthguidances.com. (2016). Dry Heaving: Causes & Home Remedies. Retrieved from Healthguidances.com: http://www.healthguidances.com/dry-heaving/
- Bowen, R. (1996, April 10). Physiology of Vomiting. Retrieved from Colorado State University: http://arbl.cvmbs.colostate.edu/hbooks/pathphys/digestion/stomach/vomiting.html




Wonderful website. A lot of useful information here.
I’m sending it to several pals ans also sharing in delicious.
And of course, thank you for your sweat!