What are pinpoint pupils?
The regular diameter of pupils ranges from 2mm to 4mm. When a patient’s pupil holds a diameter smaller than 2mm, clinicians might diagnose that patient with miosis or pinpoint pupils.
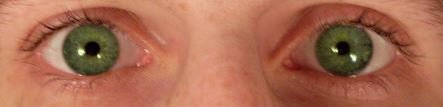
The pupil is located at the exact center of the eye and it is perceived as a black circle. What is popularly known as “eye color” is actually called iris. This structure is made of small smooth muscle fibers and these fibers are responsible for the size of the pupil.
Whenever a ray of light hits the eye, it passes through the cornea all the way into the anterior chamber. According to the intensity and quality of the light that is passing through the eye, the muscle fibers of the iris will either relax or contract in order to keep the posterior chamber, and particularly the retina, safe from photogenic harm.
That is why pupils get wider during the night or while the person is in a dark room with dim lights, and they get small when exposed to a direct source of light like the one on the environment during daytime, or the one coming from the doctor’s flashlight.
These fluctuations in pupil diameter when exposed to different lighting is normal and called Photopupillary Reflex or Pupilary Light Reflex (PLR).
Pinpoint pupils are pupils with a fixed diameter smaller than 2mm that do not respond accordingly to changes in lighting. Frequently, PLR is not present.[2]
What do pinpoint pupils mean?
Pinpoint pupils with no PLR are usually a translation of a neurological abnormality. Like it was stated in the previous point, it is completely normal to have small pupils while out on the daylight or while being exposed to a direct source of light. It is also frequent to find newborns and the elder have smaller pupils than usual, with a slowest PLR time. [2, 3]
However, pupils should go back to its normal or usual diameter after the direct source of light is removed or once the person enters a dim room.
If a person’s pupils do not change sizes after an alteration of environmental lighting, it means that the regulatory iris mechanism for pupil diameter control is altered in one way or another, mainly because of central nervous system alterations.
Constant miosis is not normal and it is a sign of neurological abnormalities.
Symptoms
- Night blindness.
- Near-vision difficulty.
- Reading problems.
Causes
The assessment of probable causes of miotic pupils depends on a variety of criteria. First, if the miotic or pinpoint pupil is non-reactive, minimally reactive or normally reactive. Furthermore, strictly unilateral miosis might respond to malignant and serious causes such as tumors or acute ophthalmic nerve compression by some extrinsic cause.
However, bilateral pinpoint pupils are the most frequent form presentations, and this might be attributed to many causes, such as:
Opioid abuse
Opioids are substances that act like opioid receptors in order to induce morphine-like effects both in the spinal cord and the central nervous system in order to reduce the intensity of pain-signal perception (drugabuse.gov).
Some opioid derivate drugs are used among clinicians to treat different diseases such as chronic pain or palliative treatment of pain for cancer patients. Such is the case for hydrocodone, oxycodone, codeine and morphine.
Despite these drugs being legal if obtained by the regular protocol involving a physician and a pharmaceutical distributor, there has been reported misuse of these legal drugs due to its dependence-inducing effects. Illegal drugs such as heroin are also opioids.
Recreational use of both prescription and illegal opioids are a public health issue that has been addressed for decades without significant results. When a patient arrives to an emergency room after a heroine or oxycodone overdose, they usually walk in either dizzy or unable to stand, showing speech fluidity limitations and pinpoint pupils.
Intoxication by organophosphates and other chemicals
Given that the main control of the iris smooth muscle is in charge of the parasympathetic autonomous nervous systems, all chemicals that could potentially cause parasympathetic over-stimulation will cause pinpoint pupils.
Organophosphates are commonly used as pesticides in agriculture, so epidemic data about the person showing pinpoint pupils is very important. An agriculture or a farm worker that is exposed to pesticides containing phosphorus will be more likely to be suffering from organophosphates than a heroin overdose.
Pontine hemorrhage
This is, fortunately, the rarest cause of pinpoint pupils. An active intracranial hemorrhage will usually present itself clinically with an acute, very intense pain and loss of consciousness. However, if the hemorrhage is not substantial or due to an abrupt cause and if it is mainly located at the pons (i.e. a special structure of the brain stem that connects and redirections signals from brain cortex to the cerebellum and other structures) it usually manifests itself with pinpoint pupils and nothing else.
Depending on the extension and distribution of the pontine hemorrhage, miosis can be either bilateral and symmetrical or unilateral and asymmetrical.
Microcoria
This rare condition affects 1 in 2000 people and it consists on a genetic autosomical disease causing pupils to remain miotic throughout the life of the person. It is also related to other functional abnormalities, such as juvenile glaucoma and nephrotic syndrome. [3]
Treatment
Miosis or pinpoint pupils do not constitute a disease by themselves—they are a symptom of a subjacent neurological alteration. Therefore, there is no gold standard treatment for pinpoint pupils. Instead, doctors are compelled to treat the original problem that is causing pupils to be miotic. [2]
For instance, in an opioid overdose, it is imperative to give the patient intravenous fluids and further assistance regarding his or her drug dependence. If an intracranial hemorrhage is suspected, patients should be submitted to further exams such as MRI in order for doctors to be able to plan the exact medical conduct. If the issue is congenital, like in the case of microcoria, surgery is recommended and palliative and life quality enhancement measurements should follow.
Reference links:
- Misuse of Prescription Drugs https://www.drugabuse.gov/publications/research-reports/misuse-prescription-drugs/which-classes-prescription-drugs-are-commonly-misused
- Miosis at WebMD http://www.webmd.com/eye-health/eye_miosis_facts#1
- Microcoria http://www.rightdiagnosis.com/m/microcoria_congenital/prevalence.htm